IL-37 overexpression promotes endometrial regenerative cell-mediated inhibition of cardiac allograft rejection
- PMID: 35841010
- PMCID: PMC9284885
- DOI: 10.1186/s13287-022-02982-1
IL-37 overexpression promotes endometrial regenerative cell-mediated inhibition of cardiac allograft rejection
Abstract
Background: Endometrial regenerative cells (ERCs) play an important role in attenuation of acute allograft rejection, while their effects are limited. IL-37, a newly discovered immunoregulatory cytokine of the IL-1 family, can regulate both innate and adaptive immunity. Whether IL-37 overexpression can enhance the therapeutic effects of ERCs in inhibition of acute cardiac allograft rejection remains unknown and will be explored in this study.
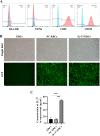
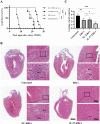
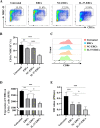
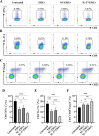
Methods: C57BL/6 mice recipients receiving BALB/c mouse heterotopic heart allografts were randomly divided into the phosphate-buffered saline (untreated), ERC treated, negative lentiviral control ERC (NC-ERC) treated, and IL-37 overexpressing ERC (IL-37-ERC) treated groups. Graft pathological changes were assessed by H&E staining. The intra-graft cell infiltration and splenic immune cell populations were analyzed by immunohistochemistry and flow cytometry, respectively. The stimulatory property of recipient DCs was tested by an MLR assay. Furthermore, serum cytokine profiles of recipients were measured by ELISA assay.
Results: Mice treated with IL-37-ERCs achieved significantly prolonged allograft survival compared with the ERC-treated group. Compared with all the other control groups, IL-37-ERC-treated group showed mitigated inflammatory response, a significant increase in tolerogenic dendritic cells (Tol-DCs), regulatory T cells (Tregs) in the grafts and spleens, while a reduction of Th1 and Th17 cell population. Additionally, there was a significant upregulation of immunoregulatory IL-10, while a reduction of IFN-γ, IL-17A, IL-12 was detected in the sera of IL-37-ERC-treated recipients.
Conclusion: IL-37 overexpression can promote the therapeutic effects of ERCs to inhibit acute allograft rejection and further prolong graft survival. This study suggests that gene-modified ERCs overexpressing IL-37 may pave the way for novel therapeutic options in the field of transplantation.
Keywords: Acute allograft rejection; Endometrial regenerative cells; Interleukin-37; Mice.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CD73-expressing endometrial regenerative cell-derived exosomes mitigate acute cardiac allograft rejection through regulating adenosine metabolism in mice.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025 Jun 2;16(1):277. doi: 10.1186/s13287-025-04398-z. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40457389 Free PMC article.
-
Endometrial regeneration cell-derived exosomes loaded with siSLAMF6 inhibit cardiac allograft rejection through the suppression of desialylation modification.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024 Oct 1;29(1):128. doi: 10.1186/s11658-024-00645-y. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024. PMID: 39354345 Free PMC article.
-
CD73 expression is critical to therapeutic effects of human endometrial regenerative cells in inhibition of cardiac allograft rejection in mice.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2021 Mar;10(3):465-478. doi: 10.1002/sctm.20-0154. Epub 2020 Oct 30. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 33124777 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting IL-6 to prevent cardiac allograft rejection.Am J Transplant. 2022 Dec;22 Suppl 4(Suppl 4):12-17. doi: 10.1111/ajt.17206. Am J Transplant. 2022. PMID: 36453706 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IL-6 Directed Therapy in Transplantation.Curr Transplant Rep. 2021;8(3):191-204. doi: 10.1007/s40472-021-00331-4. Epub 2021 Jun 3. Curr Transplant Rep. 2021. PMID: 34099967 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CD73 mediates the therapeutic effects of endometrial regenerative cells in concanavalin A-induced hepatitis by regulating CD4+ T cells.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023 Sep 29;14(1):277. doi: 10.1186/s13287-023-03505-2. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 37775797 Free PMC article.
-
IL‑37 suppresses macrophage ferroptosis to attenuate diabetic atherosclerosis via the NRF2 pathway.Exp Ther Med. 2023 May 3;25(6):289. doi: 10.3892/etm.2023.11988. eCollection 2023 Jun. Exp Ther Med. 2023. PMID: 37206550 Free PMC article.
-
CD73-expressing endometrial regenerative cell-derived exosomes mitigate acute cardiac allograft rejection through regulating adenosine metabolism in mice.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025 Jun 2;16(1):277. doi: 10.1186/s13287-025-04398-z. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40457389 Free PMC article.
-
Endometrial regeneration cell-derived exosomes loaded with siSLAMF6 inhibit cardiac allograft rejection through the suppression of desialylation modification.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024 Oct 1;29(1):128. doi: 10.1186/s11658-024-00645-y. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024. PMID: 39354345 Free PMC article.
References
-
- OPTN/SRTR 2019 annual data report: introduction. Am J Transplant. 2021;21(Suppl 2):11–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

