The shared genetic basis of mood instability and psychiatric disorders: A cross-trait genome-wide association analysis
- PMID: 35841185
- PMCID: PMC9541703
- DOI: 10.1002/ajmg.b.32907
The shared genetic basis of mood instability and psychiatric disorders: A cross-trait genome-wide association analysis
Abstract
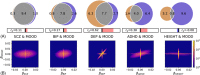
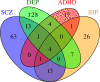
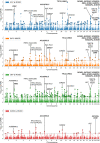
Recent genome-wide association studies of mood instability (MOOD) have found significant positive genetic correlation with major depression (DEP) and weak correlations with other psychiatric disorders. We investigated the polygenic overlap between MOOD and psychiatric disorders beyond genetic correlation to better characterize putative shared genetic determinants. GWAS summary statistics for schizophrenia (SCZ, n = 105,318), bipolar disorder (BIP, n = 413,466), DEP (n = 450,619), attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD, n = 53,293), and MOOD (n = 363,705) were analyzed using the bivariate causal mixture model and conjunctional false discovery rate methods. MOOD correlated positively with all psychiatric disorders, but with wide variation in strength (rg = 0.10-0.62). Of 10.4 K genomic variants influencing MOOD, 4 K-9.4 K influenced psychiatric disorders. Furthermore, MOOD was jointly associated with DEP at 163 loci, SCZ at 110, BIP at 60 and ADHD at 25. Fifty-three jointly associated loci were overlapping across two or more disorders, seven of which had discordant effect directions on psychiatric disorders. Genes mapped to loci associated with MOOD and all four disorders were enriched in a single gene-set, "synapse organization." The extensive polygenic overlap indicates shared molecular underpinnings across MOOD and psychiatric disorders. However, distinct patterns of genetic correlation and effect directions may relate to differences in the core clinical features of each disorder.
Keywords: ADHD; bipolar disorder; genetic overlap; major depression; mood instability; schizophrenia.
© 2022 The Authors. American Journal of Medical Genetics Part B: Neuropsychiatric Genetics published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
O.A.A. has received speaker's honorarium from Lundbeck and is a consultant for Healthlytix. A.M.D. is a founder of and holds equity interest in CorTechs Labs and serves on its scientific advisory board. He is also a member of the Scientific Advisory Board of Healthlytix and receives research funding from General Electric Healthcare (GEHC). The terms of these arrangements have been reviewed and approved by the University of California, San Diego in accordance with its conflict‐of‐interest policies. Remaining authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Shared Genetic Loci Between Body Mass Index and Major Psychiatric Disorders: A Genome-wide Association Study.JAMA Psychiatry. 2020 May 1;77(5):503-512. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2019.4188. JAMA Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 31913414 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of novel genomic loci for anxiety symptoms and extensive genetic overlap with psychiatric disorders.Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2024 Dec;78(12):783-791. doi: 10.1111/pcn.13742. Epub 2024 Sep 20. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39301620 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis in UK Biobank identifies four loci associated with mood instability and genetic correlation with major depressive disorder, anxiety disorder and schizophrenia.Transl Psychiatry. 2017 Nov 30;7(11):1264. doi: 10.1038/s41398-017-0012-7. Transl Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 29187730 Free PMC article.
-
The emerging pattern of shared polygenic architecture of psychiatric disorders, conceptual and methodological challenges.Psychiatr Genet. 2019 Oct;29(5):152-159. doi: 10.1097/YPG.0000000000000234. Psychiatr Genet. 2019. PMID: 31464996 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[New directions in psychiatric genetics: Genome-wide association studies, polygenic risk score and cross-disorder analysis].Psychiatr Hung. 2019;34(4):411-418. Psychiatr Hung. 2019. PMID: 31767801 Review. Hungarian.
Cited by
-
Investigating the shared genetic architecture between depression and subcortical volumes.Nat Commun. 2024 Sep 2;15(1):7647. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-52121-y. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39223129 Free PMC article.
-
Is There a Natural, Non-addictive, and Non-anti-reward, Safe, Gene-based Solution to Treat Reward Deficiency Syndrome? KB220 Variants vs GLP-1 Analogs.J Addict Psychiatry. 2024;8(1):34-49. Epub 2024 May 20. J Addict Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 39618491 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-Specific Association Between Polymorphisms in Estrogen Receptor Alpha Gene (ESR1) and Depression: A Genome-Wide Association Study of All of Us and UK Biobank Data.Genet Epidemiol. 2025 Apr;49(3):e70004. doi: 10.1002/gepi.70004. Genet Epidemiol. 2025. PMID: 40007508
-
Divergent epigenetic responses to perinatal asphyxia in severe mental disorders.Transl Psychiatry. 2024 Jan 8;14(1):16. doi: 10.1038/s41398-023-02709-7. Transl Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38191519 Free PMC article.
-
Characterizing the Shared Genetic Underpinnings of Schizophrenia and Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors.Am J Psychiatry. 2023 Nov 1;180(11):815-826. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.20220660. Epub 2023 Sep 27. Am J Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37752828 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andreassen, O. A. , Harbo, H. F. , Wang, Y. , Thompson, W. K. , Schork, A. J. , Mattingsdal, M. , … Dale, A. M. (2015). Genetic pleiotropy between multiple sclerosis and schizophrenia but not bipolar disorder: Differential involvement of immune‐related gene loci. Molecular Psychiatry, 20(2), 207–214. 10.1038/mp.2013.195 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bahrami, S. , Hindley, G. , Winsvold, B. S. , O'Connell, K. S. , Frei, O. , Shadrin, A. , Cheng, W. , Bettella, F. , Rødevand, L. , Odegaard, K. J. , Fan, C. C. , Pirinen, M. J. , Hautakangas, H. M. , Martinsen, A. E. , Skogholt, A. H. , Brumpton, B. , Willer, C. J. , Tronvik, E. , … Kristoffersen, E. S. (2021). Dissecting the shared genetic basis of migraine and mental disorders using novel statistical tools. Brain, 145(1), 142–153. 10.1093/brain/awab267 - DOI - PMC - PubMed

