Characteristics and surgical management of pure trapdoor fracture of the orbital floor in adults: a 15-year review
- PMID: 35841436
- PMCID: PMC10684415
- DOI: 10.1007/s10006-022-01099-2
Characteristics and surgical management of pure trapdoor fracture of the orbital floor in adults: a 15-year review
Abstract
Purpose: This retrospective study aims to define the optimal timing of the surgical treatment of orbital floor trapdoor fractures (OFTFs) in adults according to clinical and radiological findings.
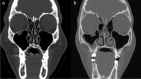
Methods: From January 2006 to December 2020, 382 patients with isolated orbital floor fracture were admitted to the Division of Maxillofacial Surgery of Turin, Italy. The criteria for inclusion were age ≥ 16 years, preoperative computed tomography showing a linear (1a) or medial hinge fracture (1b), diplopia, and 6 months of follow-up data. Aetiology and mechanism of injury, presence of post-traumatic enophthalmos and oculocardiac reflex, time between trauma occurrence and surgery [stratified as < 24 h (urgent treatment), 24-96 h (early treatment), and > 96 h (late treatment)], days of hospitalisation, and clinical outcomes were examinated.
Results: Twenty-four patients (18 males; mean age, 23.2 years) presented with OFTFs. The most common cause was sport injury (50%). Type 1a fracture was observed in eight patients (mean age, 19.5 years), type 1b fracture in 16 patients (mean age, 23.6 years). Urgent, early, and late treatments were performed in eight patients each. The mean time between trauma occurrence and surgery was 3,8 days (range: 0-17 days). Resolution of diplopia was observed 1 week after surgery in 10 patients, 1 month in 12. Diplopia persisted in 2 patient, both treated > 96 h after trauma.
Conclusion: Although the number of patients was too small to define a standard protocol, the authors recommend early treatment of adult OFTFs to promote complete resolution of diplopia.
Keywords: Adult trapdoor fracture; Epidemiology; Orbital floor fracture; Orbital trauma; Surgical timing.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources