Diagnosis and treatment of orthostatic hypotension
- PMID: 35841911
- PMCID: PMC10024337
- DOI: 10.1016/S1474-4422(22)00169-7
Diagnosis and treatment of orthostatic hypotension
Abstract
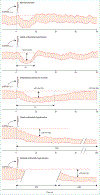
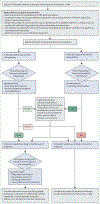
Orthostatic hypotension is an unusually large decrease in blood pressure on standing that increases the risk of adverse outcomes even when asymptomatic. Improvements in haemodynamic profiling with continuous blood pressure measurements have uncovered four major subtypes: initial orthostatic hypotension, delayed blood pressure recovery, classic orthostatic hypotension, and delayed orthostatic hypotension. Clinical presentations are varied and range from cognitive slowing with hypotensive unawareness or unexplained falls to classic presyncope and syncope. Establishing whether symptoms are due to orthostatic hypotension requires careful history taking, a thorough physical examination, and supine and upright blood pressure measurements. Management and prognosis vary according to the underlying cause, with the main distinction being whether orthostatic hypotension is neurogenic or non-neurogenic. Neurogenic orthostatic hypotension might be the earliest clinical manifestation of Parkinson's disease or related synucleinopathies, and often coincides with supine hypertension. The emerging variety of clinical presentations advocates a stepwise, individualised, and primarily non-pharmacological approach to the management of orthostatic hypotension. Such an approach could include the cessation of blood pressure lowering drugs, adoption of lifestyle measures (eg, counterpressure manoeuvres), and treatment with pharmacological agents in selected cases.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests HK is supported by grants from the Familial Dysautonomia Foundation, the Michael J Fox Foundation for Parkinson's Research, the Multiple System Atrophy Coalition, the National Institutes of Health (NIH; R01HL103988 and U54NS065736), and the US Food and Drug Administration (FDR3731–01); receives royalties from Up to Date; receives consultancy and speakers’ fees from Med-IQ, Biogen, Biohaven Pharmaceuticals, Lundbeck, Pfizer, and Theravance Biopharma; and serves as the editor-in-chief of Clinical Autonomic Research. VEC is supported by grants from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, the National Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, the International Collaboration on Repair Discoveries, the Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada, and the Craig H Neilsen Foundation. SPJ is supported by NIH grants K23HL135273 and R56HL153191. RDT reports consultancy and speakers’ fees from Union Chimique Belge, GlaxoSmithKline, Theravance, Novartis, and Zogenix; and grants from the Dutch National Epilepsy Fund, the Michael J Fox Foundation for Parkinson's Research (MJFF-020200), Christelijke Vereniging voor de Verpleging van Lijders aan Epilepsie, Medtronic, New Life Wearables, and The Netherlands Organisation for Health Research and Development (114025101). All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Mol A, Bui Hoang PTS, Sharmin S, et al. Orthostatic hypotension and falls in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Med Dir Assoc 2019; 20: 589–97.e5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

