Analyzing the Spatial Randomness in the Distribution of Acquired Melanocytic Neoplasms
- PMID: 35841946
- PMCID: PMC10475172
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jid.2022.06.011
Analyzing the Spatial Randomness in the Distribution of Acquired Melanocytic Neoplasms
Abstract
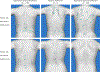
On the basis of the clinical impression and current knowledge, acquired melanocytic nevi and melanomas may not occur in random localizations. The goal of this study was to identify whether their distribution on the back is random and whether the location of melanoma correlates with its adjacent lesions. Therefore, patient-level and lesion-level spatial analyses were performed using the Clark‒Evans test for complete spatial randomness. A total of 311 patients with three-dimensional total body photography (average age of 40.08 [30‒49] years; male/female ratio: 128/183) with 5,108 eligible lesions in total were included in the study (mean sum of eligible lesions per patient of 16.42 [3‒199]). The patient-level analysis revealed that the distributions of acquired melanocytic neoplasms were more likely to deviate toward clustering than dispersion (average z-score of ‒0.55 [95% confidence interval = ‒0.69 to ‒0.41; P < 0.001]). The lesion-level analysis indicated a higher portion of melanomas (n = 57 of 72, 79.2% [95% confidence interval = 69.4‒88.9%]) appearing in proximity to neighboring melanocytic neoplasms than to nevi (n = 2,281 of 5,036, 45.3% [95% confidence interval = 43.9‒46.7%]). In conclusion, the nevi and melanomas' distribution on the back tends toward clustering as opposed to dispersion. Furthermore, melanomas are more likely to appear proximally to their neighboring neoplasms than to nevi. These findings may justify various oncogenic theories and improve diagnostic methodology.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
Allan C. Halpern: Canfield Scientific, Inc.-consultant; SciBase-advisory board. The rest authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures
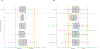
References
-
- Alomari AK, Miedema JR, Carter MD, Harms PW, Lowe L, Durham AB et al. DNA copy number changes correlate with clinical behavior in melanocytic neoplasms: proposal of an algorithmic approach. Mod Pathol. 2020. Jul;33(7):1307–17. - PubMed
-
- Barlow JO, Maize J Sr, Lang PG. The density and distribution of melanocytes adjacent to melanoma and nonmelanoma skin cancers. Dermatol Surg. 2007. Feb;33(2):199–207. - PubMed
-
- Bataille V, Snieder H, MacGregor AJ, Sasieni P, Spector TD. Genetics of risk factors for melanoma: an adult twin study of nevi and freckles. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000. Mar 15;92(6):457–63. - PubMed
-
- Bauer J, Büttner P, Wiecker TS, Luther H, Garbe C. Risk factors of incident melanocytic nevi: a longitudinal study in a cohort of 1,232 young German children. Int J Cancer. 2005. May 20;115(1):121–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

