SynthStrip: skull-stripping for any brain image
- PMID: 35842095
- PMCID: PMC9465771
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2022.119474
SynthStrip: skull-stripping for any brain image
Abstract
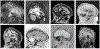
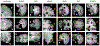
The removal of non-brain signal from magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data, known as skull-stripping, is an integral component of many neuroimage analysis streams. Despite their abundance, popular classical skull-stripping methods are usually tailored to images with specific acquisition properties, namely near-isotropic resolution and T1-weighted (T1w) MRI contrast, which are prevalent in research settings. As a result, existing tools tend to adapt poorly to other image types, such as stacks of thick slices acquired with fast spin-echo (FSE) MRI that are common in the clinic. While learning-based approaches for brain extraction have gained traction in recent years, these methods face a similar burden, as they are only effective for image types seen during the training procedure. To achieve robust skull-stripping across a landscape of imaging protocols, we introduce SynthStrip, a rapid, learning-based brain-extraction tool. By leveraging anatomical segmentations to generate an entirely synthetic training dataset with anatomies, intensity distributions, and artifacts that far exceed the realistic range of medical images, SynthStrip learns to successfully generalize to a variety of real acquired brain images, removing the need for training data with target contrasts. We demonstrate the efficacy of SynthStrip for a diverse set of image acquisitions and resolutions across subject populations, ranging from newborn to adult. We show substantial improvements in accuracy over popular skull-stripping baselines - all with a single trained model. Our method and labeled evaluation data are available at https://w3id.org/synthstrip.
Keywords: Brain extraction; Deep learning; Image synthesis; MRI-contrast agnosticism; Skull stripping.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest Bruce Fischl has a financial interest in CorticoMetrics, a company whose medical pursuits focus on brain imaging and measurement technologies. This interest is reviewed and managed by Massachusetts General Hospital and Mass General Brigham in accordance with their conflict-of-interest policies. The authors declare that they have no other known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

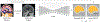



References
-
- Andrade N, Faria FA, Cappabianco FAM, 2018. A practical review on medical image registration: From rigid to deep learning based approaches. In: 2018 31st SIBGRAPI Conference on Graphics, Patterns and Images (SIBGRAPI). IEEE, pp. 463–470.
-
- Arsigny V, Commowick O, Pennec X, Ayache N, 2006. A log-euclidean framework for statistics on diffeomorphisms. In: MICCAI: Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Interventions. Springer, pp. 924–931. - PubMed
-
- Ashburner J, 2007. A fast diffeomorphic image registration algorithm. Neuroimage 38 (1), 95–113 . - PubMed
-
- Ashburner J, 2009. Preparing fMRI Data for Statistical Analysis. In: fMRI techniques and protocols. Springer, pp. 151–178.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R21 EB018907/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG016495/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 MH123195/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 MH121885/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS105820/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB019956/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AG064027/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P41 EB030006/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH117023/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR023043/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH093765/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS070963/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR019307/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG070988/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB023281/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- K99 HD101553/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P41 EB015896/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS083534/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR023401/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

