Early life stress, systemic inflammation, and neural correlates of implicit emotion regulation in adolescents
- PMID: 35842188
- PMCID: PMC11824613
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbi.2022.07.007
Early life stress, systemic inflammation, and neural correlates of implicit emotion regulation in adolescents
Abstract
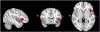
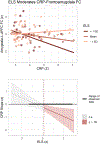
Exposure to early life stress (ELS) increases the risk for developing psychopathology; however, the mechanisms underlying this association are not clear. In this study we examined systemic inflammation as a pathway that may link exposure to stress to altered neural correlates of implicit emotion regulation in adolescents with varying levels of exposure to ELS (n = 83; 52 females, 31 males; 15.63 ± 1.10 years). We measured ventrolateral prefrontal cortex (vlPFC) activation and functional connectivity (FC) between the bilateral amygdala and the vlPFC as adolescents completed an affect labeling task in the scanner and assessed concentrations of C-reactive protein (CRP) using a dried blood spot protocol. We found that CRP levels were negatively associated with vlPFC activation during implicit regulation of negatively-valenced stimuli, and that cumulative severity of ELS exposure moderated this neuroimmune association. Severity of ELS also significantly moderated the association between CRP levels and FC between the bilateral amygdala and l-vlPFC during implicit emotion regulation: in adolescents who had been exposed to more severe ELS, higher CRP was associated with more negative frontoamygdala FC during implicit regulation of negatively-valenced stimuli. Thus, ELS may disrupt the normative association between the immune system and the neural processes that underlie socioemotional functioning potentially increasing adolescents' risk for maladaptive outcomes.
Keywords: Adolescence; C-reactive protein; Early life stress; Emotion regulation; Inflammation; fMRI.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The association between early life stress and prefrontal cortex activation during implicit emotion regulation is moderated by sex in early adolescence.Dev Psychopathol. 2017 Dec;29(5):1851-1864. doi: 10.1017/S0954579417001444. Dev Psychopathol. 2017. PMID: 29162186 Free PMC article.
-
Early Life Stress, Frontoamygdala Connectivity, and Biological Aging in Adolescence: A Longitudinal Investigation.Cereb Cortex. 2020 Jun 1;30(7):4269-4280. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhaa057. Cereb Cortex. 2020. PMID: 32215605 Free PMC article.
-
Differential functional connectivity within an emotion regulation neural network among individuals resilient and susceptible to the depressogenic effects of early life stress.Psychol Med. 2013 Mar;43(3):507-18. doi: 10.1017/S0033291712001390. Epub 2012 Jul 10. Psychol Med. 2013. PMID: 22781311
-
The Common and Different Neural Bases of Distraction and Reinterpretation: A Meta-Analysis of fMRI Studies.J Integr Neurosci. 2022 Jun 1;21(4):107. doi: 10.31083/j.jin2104107. J Integr Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35864759 Review.
-
Neural Circuitry of Impaired Emotion Regulation in Substance Use Disorders.Am J Psychiatry. 2016 Apr 1;173(4):344-61. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2015.15060710. Epub 2016 Jan 15. Am J Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 26771738 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Psychological stress: neuroimmune roles in periodontal disease.Odontology. 2023 Jul;111(3):554-564. doi: 10.1007/s10266-022-00768-8. Epub 2022 Nov 28. Odontology. 2023. PMID: 36437431 Review.
-
Impact of social reward on stress circuit function and regulation: Path differences between value affirmation and emotional support.Int J Clin Health Psychol. 2024 Jul-Sep;24(3):100499. doi: 10.1016/j.ijchp.2024.100499. Epub 2024 Sep 10. Int J Clin Health Psychol. 2024. PMID: 39308781 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal exposure to maternal disadvantage-related inflammatory biomarkers: associations with neonatal white matter microstructure.Transl Psychiatry. 2024 Feb 2;14(1):72. doi: 10.1038/s41398-024-02782-6. Transl Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38307841 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating psychosocial factors and systemic inflammation using dried blood spots: a scoping review.Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2025 Jun 13. doi: 10.1007/s00127-025-02941-0. Online ahead of print. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2025. PMID: 40514590 Review.
-
Effects of Pollution Burden on Neural Function During Implicit Emotion Regulation and Longitudinal Changes in Depressive Symptoms in Adolescents.Biol Psychiatry Glob Open Sci. 2024 Apr 26;4(4):100322. doi: 10.1016/j.bpsgos.2024.100322. eCollection 2024 Jul. Biol Psychiatry Glob Open Sci. 2024. PMID: 38957313 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aiken LS, West SG, Reno RR, 1991. Multiple Regression: Testing and Interpreting Interactions. SAGE.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

