Three-dimensional conditional generative adversarial network-based virtual thin-slice technique for the morphological evaluation of the spine
- PMID: 35842451
- PMCID: PMC9288435
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-16637-x
Three-dimensional conditional generative adversarial network-based virtual thin-slice technique for the morphological evaluation of the spine
Abstract
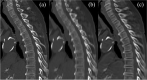
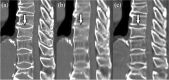
Virtual thin-slice (VTS) technique is a generative adversarial network-based algorithm that can generate virtual 1-mm-thick CT images from images of 3-10-mm thickness. We evaluated the performance of VTS technique for assessment of the spine. VTS was applied to 4-mm-thick CT images of 73 patients, and the visibility of intervertebral spaces was evaluated on the 4-mm-thick and VTS images. The heights of vertebrae measured on sagittal images reconstructed from the 4-mm-thick images and VTS images were compared with those measured on images reconstructed from 1-mm-thick images. Diagnostic performance for the detection of compression fractures was also compared. The intervertebral spaces were significantly more visible on the VTS images than on the 4-mm-thick images (P < 0.001). The absolute value of the measured difference in mean vertebral height between the VTS and 1-mm-thick images was smaller than that between the 4-mm-thick and 1-mm-thick images (P < 0.01-0.54). The diagnostic performance of the VTS images for detecting compression fracture was significantly lower than that of the 4-mm-thick images for one reader (P = 0.02). VTS technique enabled the identification of each vertebral body, and enabled accurate measurement of vertebral height. However, this technique is not suitable for diagnosing compression fractures.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
S.K. has received funding support from FUJIFILM Corporation. J.M., A.K., and Y.K. are employees of FUJIFILM Corporation. A.N., M.H., H.O., T.O., H.F., K.O. and N.T. state that they have not received any funding for this work.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Dual-energy CT virtual non-calcium technique for detection of bone marrow edema in patients with vertebral fractures: A prospective feasibility study on a single- source volume CT scanner.Eur J Radiol. 2017 Feb;87:59-65. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2016.12.008. Epub 2016 Dec 12. Eur J Radiol. 2017. PMID: 28065376
-
Dual-Energy CT-based Display of Bone Marrow Edema in Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures: Impact on Diagnostic Accuracy of Radiologists with Varying Levels of Experience in Correlation to MR Imaging.Radiology. 2016 Aug;280(2):510-9. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2016150472. Epub 2016 Feb 29. Radiology. 2016. PMID: 26928067
-
Single-source dual-energy computed tomography for the assessment of bone marrow oedema in vertebral compression fractures: a prospective diagnostic accuracy study.Eur Radiol. 2019 Jan;29(1):31-39. doi: 10.1007/s00330-018-5568-y. Epub 2018 Jun 15. Eur Radiol. 2019. PMID: 29948088
-
Generative adversarial networks for spine imaging: A critical review of current applications.Eur J Radiol. 2024 Feb;171:111313. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2024.111313. Epub 2024 Jan 12. Eur J Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38237518 Review.
-
Pearls for Interpreting Computed Tomography of the Cervical Spine in Trauma.Radiol Clin North Am. 2015 Jul;53(4):657-74, vii. doi: 10.1016/j.rcl.2015.02.015. Radiol Clin North Am. 2015. PMID: 26046504 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of Deep Learning 3D CT Super-Resolution on AI-Based Pulmonary Nodule Characterization.Tomography. 2025 Jan 27;11(2):13. doi: 10.3390/tomography11020013. Tomography. 2025. PMID: 39997996 Free PMC article.
-
Improved Consistency of Lung Nodule Categorization in CT Scans with Heterogeneous Slice Thickness by Deep Learning-Based 3D Super-Resolution.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Dec 28;15(1):50. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15010050. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39795578 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

