Development of the H3N2 influenza microneedle vaccine for cross-protection against antigenic variants
- PMID: 35842468
- PMCID: PMC9287697
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-16365-2
Development of the H3N2 influenza microneedle vaccine for cross-protection against antigenic variants
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Development of the H3N2 influenza microneedle vaccine for cross-protection against antigenic variants.Sci Rep. 2022 Oct 3;12(1):16540. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-20913-1. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36192424 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
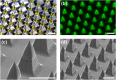
Due to the continuously mutating nature of the H3N2 virus, two aspects were considered when preparing the H3N2 microneedle vaccines: (1) rapid preparation and (2) cross-protection against multiple antigenic variants. Previous methods of measuring hemagglutinin (HA) content required the standard antibody, thus rapid preparation of H3N2 microneedle vaccines targeting the mutant H3N2 was delayed as a result of lacking a standard antibody. In this study, H3N2 microneedle vaccines were prepared by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) without the use of an antibody, and the cross-protection of the vaccines against several antigenic variants was observed. The HA content measured by HPLC was compared with that measured by ELISA to observe the accuracy of the HPLC analysis of HA content. The cross-protection afforded by the H3N2 microneedle vaccines was evaluated against several antigenic variants in mice. Microneedle vaccines for the 2019-20 seasonal H3N2 influenza virus (19-20 A/KS/17) were prepared using a dip-coating process. The cross-protection of 19-20 A/KS/17 H3N2 microneedle vaccines against the 2015-16 seasonal H3N2 influenza virus in mice was investigated by monitoring body weight changes and survival rate. The neutralizing antibody against several H3N2 antigenic variants was evaluated using the plaque reduction neutralization test (PRNT). HA content in the solid microneedle vaccine formulation with trehalose post-exposure at 40℃ for 24 h was 48% and 43% from the initial HA content by HPLC and ELISA, respectively. The vaccine was administered to two groups of mice, one by microneedles and the other by intramuscular injection (IM). In vivo efficacies in the two groups were found to be similar, and cross-protection efficacy was also similar in both groups. HPLC exhibited good diagnostic performance with H3N2 microneedle vaccines and good agreement with ELISA. The H3N2 microneedle vaccines elicited a cross-protective immune response against the H3N2 antigenic variants. Here, we propose the use of HPLC for a more rapid approach in preparing H3N2 microneedle vaccines targeting H3N2 virus variants.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
PJH is an inventor of patents that have been licensed to companies developing microneedle-based products, is a shareholder of companies developing microneedle-based products.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Computationally Optimized Broadly Reactive Hemagglutinin Elicits Hemagglutination Inhibition Antibodies against a Panel of H3N2 Influenza Virus Cocirculating Variants.J Virol. 2017 Nov 30;91(24):e01581-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01581-17. Print 2017 Dec 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28978710 Free PMC article.
-
Elicitation of Protective Antibodies against 20 Years of Future H3N2 Cocirculating Influenza Virus Variants in Ferrets Preimmune to Historical H3N2 Influenza Viruses.J Virol. 2019 Jan 17;93(3):e00946-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00946-18. Print 2019 Feb 1. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30429350 Free PMC article.
-
A virus-like particle vaccination strategy expands its tolerance to H3N2 antigenic drift by enhancing neutralizing antibodies against hemagglutinin stalk.Antiviral Res. 2017 Apr;140:62-75. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2017.01.010. Epub 2017 Jan 14. Antiviral Res. 2017. PMID: 28093338
-
Evaluation of Next-Generation H3 Influenza Vaccines in Ferrets Pre-Immune to Historical H3N2 Viruses.Front Immunol. 2021 Aug 12;12:707339. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.707339. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34475872 Free PMC article.
-
Bivalent H1 and H3 COBRA Recombinant Hemagglutinin Vaccines Elicit Seroprotective Antibodies against H1N1 and H3N2 Influenza Viruses from 2009 to 2019.J Virol. 2022 Apr 13;96(7):e0165221. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01652-21. Epub 2022 Mar 15. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 35289635 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Advances in Polysaccharide-Based Microneedle Systems for the Treatment of Ocular Diseases.Nanomicro Lett. 2024 Aug 13;16(1):268. doi: 10.1007/s40820-024-01477-3. Nanomicro Lett. 2024. PMID: 39136800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toward a solid microneedle patch for rapid and enhanced local analgesic action.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2024 Jul;14(7):1810-1819. doi: 10.1007/s13346-023-01486-6. Epub 2024 Jan 18. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 38236507
-
Advances in the Functionalization of Vaccine Delivery Systems: Innovative Strategies and Translational Perspectives.Pharmaceutics. 2025 May 12;17(5):640. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17050640. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40430931 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic synthetic and natural materials for immunoengineering.Chem Soc Rev. 2024 Feb 19;53(4):1789-1822. doi: 10.1039/d3cs00805c. Chem Soc Rev. 2024. PMID: 38170619 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unique advantages and applications of polysaccharide microneedles as drug delivery materials and in treatment of skin diseases.Nanoscale Adv. 2025 Apr 12;7(12):3631-3654. doi: 10.1039/d4na01083c. eCollection 2025 Jun 10. Nanoscale Adv. 2025. PMID: 40417161 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

