Acetyl-cholinesterase-inhibitors slow cognitive decline and decrease overall mortality in older patients with dementia
- PMID: 35842477
- PMCID: PMC9288483
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-16476-w
Acetyl-cholinesterase-inhibitors slow cognitive decline and decrease overall mortality in older patients with dementia
Abstract
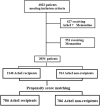
We evaluated the effect of Acetyl-cholinesterase-inhibitors (AChEIs) on cognitive decline and overall survival in a large sample of older patients with late onset Alzheimer's disease (LOAD), vascular dementia (VD) or Lewy body disease (LBD) from a real world setting. Patients with dementia enrolled between 2005 and 2020 by the "Alzheimer's Disease Research Centers" were analysed; the mean follow-up period was 7.9 years. A 1:1 propensity score matching was performed generating a cohort of 1.572 patients (786 treated [AChEIs +] and 786 not treated [AChEIs-] with AChEIs. The MMSE score was almost stable during the first 6 years of follow up in AChEIs + and then declined, while in AChEIs- it progressively declined so that at the end of follow-up (13.6 years) the average decrease in MMSE was 10.8 points in AChEIs- compared with 5.4 points in AChEIs + (p < 0.001). This trend was driven by LOAD (Δ-MMSE:-10.8 vs. -5.7 points; p < 0.001), although a similar effect was observed in VD (Δ-MMSE:-11.6 vs. -8.8; p < 0.001). No effect on cognitive status was found in LBD. At multivariate Cox regression analysis (adjusted for age, gender, dependency level and depression) a strong association between AChEIs therapy and lower all-cause mortality was observed (H.R.:0.59; 95%CI: 0.53-0.66); this was confirmed also in analyses separately conducted in LOAD, VD and LBD. Among older people with dementia, treatment with AChEIs was associated with a slower cognitive decline and with reduced mortality, after a mean follow-up of almost eight years. Our data support the effectiveness of AChEIs in older patients affected by these types of dementia.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
AC reports personal fees from Nestle, personal fees from Bristol Myers Squibb and payment /honoraria from MSD, outside the submitted work; SV reports Consulting fees from Angelini SPA and Payment/honoraria from Abbot Vifor, outside from the submitted work. MZ, GZ and LF have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- Takeda A, Loveman E, Clegg A, Kirby J, Picot J, Payne E, Green C. A systematic review of the clinical effectiveness of donepezil, rivastigmine and galantamine on cognition, quality of life and adverse events in Alzheimer's disease. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry. 2006;21:17–28. doi: 10.1002/gps.1402. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P50 AG016574/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG049638/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG016573/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005133/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005146/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG047266/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG019610/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010161/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG035982/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005134/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010129/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG053760/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010124/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG033514/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010133/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG016976/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005136/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062422/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG012300/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG008051/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG023501/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005681/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K23 AG031861/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG028383/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG008702/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG047270/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005138/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005131/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005142/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG008017/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072947/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG047366/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG013854/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG025688/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG013846/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States

