Plk2-mediated phosphorylation and translocalization of Nrf2 activates anti-inflammation through p53/Plk2/p21cip1 signaling in acute kidney injury
- PMID: 35842499
- PMCID: PMC10425522
- DOI: 10.1007/s10565-022-09741-1
Plk2-mediated phosphorylation and translocalization of Nrf2 activates anti-inflammation through p53/Plk2/p21cip1 signaling in acute kidney injury
Abstract
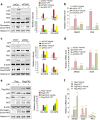
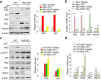
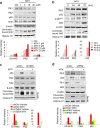
The Plk2 is a cellular stress-responsive factor that is induced in response to oxidative stress. However, the roles of Plk2 in acute kidney injury (AKI) have not been clarified. We previously found that Plk2 is an interacting factor of Nrf2 in response to cellular stress, since Plk2 is upregulated in the Nrf2-dependent network. Here, we show that the levels of p53, Plk2, p21cip1, and chromatin-bound Nrf2 were all upregulated in kidney tissues of mice or NRK52E cells treated with either cisplatin or methotrexate. Upregulation of Plk2 by p53 led to an increase of Nrf2 in both soluble and chromatin fractions in cisplatin-treated NRK52E cells. Consistently, depletion of Plk2 suppressed the levels of Nrf2. Of note, Plk2 directly phosphorylated Nrf2 at Ser40, which facilitated its interaction with p21cip1 and translocation into the nuclei for the activation of anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory factors in response to AKI. Together, these findings suggest that Plk2 may serve as an anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory regulator through the phosphorylation and activation of Nrf2 to protect kidney cells from kidney toxicants and that Plk2 and Nrf2 therefore work cooperatively for the protection and survival of kidney cells from harmful stresses.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Anti-inflammation; Nrf2; Plk2; p53.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Benetatos L, Dasoula A, Hatzimichael E, Syed N, Voukelatou M, Dranitsaris G, Bourantas KL, Crook T. Polo-like kinase 2 (SNK/PLK2) is a novel epigenetically regulated gene in acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndromes: genetic and epigenetic interactions. Ann Hematol. 2011;90:1037–1045. doi: 10.1007/s00277-011-1193-4. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

