Large tricuspid valve thrombus complicating COVID-19 pneumonia
- PMID: 35842811
- PMCID: PMC9350345
- DOI: 10.1111/jocs.16761
Large tricuspid valve thrombus complicating COVID-19 pneumonia
Abstract
Background: Hemostatic disturbances with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) can predispose to tricuspid and right heart thrombi in very rare instances.
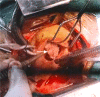
Aim: We describe a 29-year-old female patient without a previous cause of thrombosis who developed large tricuspid valve thrombus (TVT) and moderate-to-severe tricuspid regurgitation (TR) during the course of COVID-19 infection.
Materials and methods: Persistant fever and tachycardia with thrombocytopenia and high d-dimer increased the index of suspicion. The diagnosis was made by bedside transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) and cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR). Surgery was performed for thrombectomy and tricuspid valve replacement with a tissue valve.
Discussion and conclusion: Detection of TVT in COVID-19 patients on the basis of high index of suspicion, bedside TTE and noninvasive CMR helps early surgical treatment and subsequent reduction of mortality and hospital stay.
Keywords: COVID-19; cardiac magnetic resonance; hypercoagulation; thrombus; tricuspid valve.
© 2022 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Konstantinides SV, Meyer G, Becattini C, et al. ESC scientific document group: 2019 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism developed in collaboration with the European Respiratory Society (ERS). Eur Heart J. 2020;41(4):543‐603. - PubMed
-
- Johnson EM, Gage KL, Feuerlein S, Jeong D. Cardiac magnetic resonance for the evaluation of suspected cardiac thrombus: conventional and emerging techniques. J Vis Exp. 2019;148:1‐7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

