Risk of Cardiovascular Events After COVID-19
- PMID: 35843735
- PMCID: PMC9282909
- DOI: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2022.06.023
Risk of Cardiovascular Events After COVID-19
Abstract
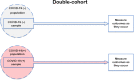
We aimed to determine absolute and relative risks of either symptomatic or asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection for late cardiovascular (CV) events and all-cause mortality. We conducted a retrospective double cohort study of patients with either symptomatic or asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection (COVID-19+ cohort) and its documented absence (COVID-19- cohort). The study investigators drew a simple random sample of records from all patients under the Oregon Health & Science University Healthcare (n = 65,585), with available COVID-19 test results, performed March 1, 2020 to September 13, 2020. Exclusion criteria were age <18 years and no established Oregon Health & Science University care. The primary outcome was a composite of CV morbidity and mortality. All-cause mortality was the secondary outcome. The study population included 1,355 patients (mean age 48.7 ± 20.5 years; 770 women [57%], 977 White non-Hispanic [72%]; 1,072 ensured [79%]; 563 with CV disease history [42%]). During a median 6 months at risk, the primary composite outcome was observed in 38 of 319 patients who were COVID-19+ (12%) and 65 of 1,036 patients who were COVID-19- (6%). In the Cox regression, adjusted for demographics, health insurance, and reason for COVID-19 testing, SARS-CoV-2 infection was associated with the risk for primary composite outcome (hazard ratio 1.71, 95% confidence interval 1.06 to 2.78, p = 0.029). Inverse probability-weighted estimation, conditioned for 31 covariates, showed that for every patient who was COVID-19+, the average time to all-cause death was 65.5 days less than when all these patients were COVID-19-: average treatment effect on the treated -65.5 (95% confidence interval -125.4 to -5.61) days, p = 0.032. In conclusion, either symptomatic or asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection is associated with an increased risk for late CV outcomes and has a causal effect on all-cause mortality in a late post-COVID-19 period.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Kuba K, Imai Y, Rao S, Gao H, Guo F, Guan B, Huan Y, Yang P, Zhang Y, Deng W, Bao L, Zhang B, Liu G, Wang Z, Chappell M, Liu Y, Zheng D, Leibbrandt A, Wada T, Slutsky AS, Liu D, Qin C, Jiang C, Penninger JM. A crucial role of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in SARS coronavirus-induced lung injury. Nat Med. 2005;11:875–879. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nalbandian A, Sehgal K, Gupta A, Madhavan MV, McGroder C, Stevens JS, Cook JR, Nordvig AS, Shalev D, Sehrawat TS, Ahluwalia N, Bikdeli B, Dietz D, Der-Nigoghossian C, Liyanage-Don N, Rosner GF, Bernstein EJ, Mohan S, Beckley AA, Seres DS, Choueiri TK, Uriel N, Ausiello JC, Accili D, Freedberg DE, Baldwin M, Schwartz A, Brodie D, Garcia CK, Elkind MSV, Connors JM, Bilezikian JP, Landry DW, Wan EY. Post-acute COVID-19 syndrome. Nat Med. 2021;27:601–615. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

