Molecular dynamics studies reveal structural and functional features of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein
- PMID: 35843871
- PMCID: PMC9350306
- DOI: 10.1002/bies.202200060
Molecular dynamics studies reveal structural and functional features of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein
Abstract
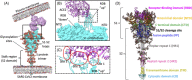
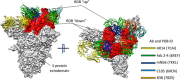
The SARS-CoV-2 virus is responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic the world experience since 2019. The protein responsible for the first steps of cell invasion, the spike protein, has probably received the most attention in light of its central role during infection. Computational approaches are among the tools employed by the scientific community in the enormous effort to study this new affliction. One of these methods, namely molecular dynamics (MD), has been used to characterize the function of the spike protein at the atomic level and unveil its structural features from a dynamic perspective. In this review, we focus on these main findings, including spike protein flexibility, rare S protein conformational changes, cryptic epitopes, the role of glycans, drug repurposing, and the effect of spike protein variants.
Keywords: SARS-Cov-2; drug repurposing; epitope; glycans; molecular dynamics; spike protein; variant.
© 2022 The Authors. BioEssays published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors do not have any conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Chan, J. F. W. , Yuan, S. , Kok, K. H. , To, K. K. W. , Chu, H. , Yang, J. , Xing, F. , Liu, J. , Yip, C. C. Y. , Poon, R. W. S. , Tsoi, H. W. , Lo, S. K. F. , Chan, K. H. , Poon, V. K. M. , Chan, W. M. , Ip, J. D. , Cai, J. P. , Cheng, V. C. , … Yuen, K. Y. (2020). A familial cluster of pneumonia associated with the 2019 novel coronavirus indicating person‐to‐person transmission: A study of a family cluster. Lancet, 395(10223), 514–523. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wu, F. , Zhao, S. , Yu, B. , Chen, Y. M. , Wang, W. , Song, Z. G. , Hu, Y. , Tao, Z.‐W. , Tian, J. H. , Pei, Y. Y. , Yuan, M.‐L. , Zhang, Y.‐L. , Dai, F.‐H. , Liu, Y. , Wang, Q.‐M. , Zheng, J. J. , Xu, L. , Holmes, E. C. , & Zhang, Y. Z. (2020). A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China. Nature, 579(7798), 265–269. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhou, P. , Yang, X. L. , Wang, X. G. , Hu, B. , Zhang, L. , Zhang, W. , Si, H. R. , Zhu, Y. , Li, B. , Huang, C. L. , Chen, H. D. , Chen, J. , Luo, Y. , Guo, H. , Jiang, R.‐D. , Liu, M. Q. , Chen, Y. , Shen, X.‐R. , Wang, X. , … Shi, Z.‐L. (2020). A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature, 579(7798), 270–273. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Siddell, S. G. (1995). The coronaviridae: An introduction. In Siddell S. G. (Ed.), The Coronaviridae (pp. 1–10). Springer US.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

