Diagnostic accuracy of palpation versus ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration biopsy for diagnosis of malignancy in thyroid nodules: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 35843955
- PMCID: PMC9290285
- DOI: 10.1186/s12902-022-01085-5
Diagnostic accuracy of palpation versus ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration biopsy for diagnosis of malignancy in thyroid nodules: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
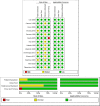
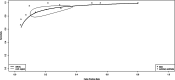
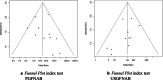
Thyroid nodule is a common health problem in endocrinology. Thyroid fine-needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB) cytology performed by palpation guided FNAB (PGFNAB) and ultrasound-guided FNAB (USGFNAB) are the preferred examinations for the diagnosis of thyroid cancer and part of the integration of the current thyroid nodule assessment. Although studies have shown USGFNAB to be more accurate than PGFNAB, inconsistencies from several studies and clinical guidelines still exist.The purpose of this study is to compare the diagnostic accuracy of Palpation versus Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy in diagnosing malignancy of thyroid nodules.The systematic review and meta-analysis were prepared based on the PRISMA standards. Literature searches were carried out on three online databases (Pubmed/MEDLINE, Embase, and Proquest) and grey literatures. Data extraction was carried out manually from various studies that met the eligibility, followed by analysis to obtain pooled data on sensitivity, specificity, Diagnostic Odds Ratio (DOR) and Area Under Curve (AUC), and the comparison of the two methods.Total of 2517 articles were obtained, with 11 studies were included in this systematic review. The total sample was 2382, including 1128 subjects using PGFNAB and 1254 subjects using USGFNAB. The risk of bias was assessed using QUADAS-2 with mild-moderate results. The results of sensitivity, specificity, AUC and DOR in diagnosing thyroid nodules using PGFNAB were 76% (95% CI, 49-89%), 77% (95% CI, 56-95%), 0.827 and 11.6 (95% CI, 6-21) respectively. The results of sensitivity, specificity, AUC and DOR in diagnosing thyroid nodules using USGFNAB were 90% (95% CI, 81-95%), 80% (95% CI, 66-89%), 0.92 and 40 (95% CI, 23-69), respectively the results of the comparison test between PGFNAB and USGFNAB; Tsens USGFNAB of 0.99 (p = 0.023), AUC difference test of 0.093 (p = 0.000023).The diagnostic accuracy of USGFNAB is higher than PGFNAB in diagnosing malignancy of thyroid nodules. If it is accessible, the author recommends using USGFNAB as a diagnostic tool for thyroid nodules.
Keywords: Fine-needle aspiration biopsy; Palpable versus USG guided; Thyroid nodules.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to disclose in this meta-analysis. The source of funding for the meta-analysis process comes from the author himself.
Figures
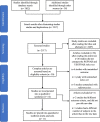


References
-
- Haugen BR, Alexander EK, Bible KC, Doherty GM, Mandel SJ, Nikiforov YE, et al. 2015 American Thyroid Association management guidelines for adult patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer: the American Thyroid Association guidelines task force on thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer. Thyroid. 2016;26(1):1–133. doi: 10.1089/thy.2015.0020. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Saksono D, Soewondo P, Subekti I, Soebardi S, Darmowidjoyo B, Purnamasari D, Tarigan TJE, Wisnu WTD. Petunjuk praktis pengelolaan nodul tiroid. Jakarta Pusat: PERKENI; 2018. pp. 1–43.
-
- Pemayun T. Current diagnosis and management of thyroid nodules. Acta Med Indones-Indones J Intern Med. 2016;48(3):247–57. - PubMed
-
- Ospina NS, Brito JP, Maraka S, Espinosa de Ycaza AE, Rodriguez-Gutierrez R, Gionfriddo MR, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration biopsy for thyroid malignancy: systematic review and meta-analysis. Endocrine. 2016;53(3):651–661. doi: 10.1007/s12020-016-0921-x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

