Forgetting Alcohol: A Double-Blind, Randomized Controlled Trial Investigating Memory Inhibition Training in Young Binge Drinkers
- PMID: 35844233
- PMCID: PMC9278062
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2022.914213
Forgetting Alcohol: A Double-Blind, Randomized Controlled Trial Investigating Memory Inhibition Training in Young Binge Drinkers
Abstract
Background: Binge Drinking (BD) has been associated with altered inhibitory control and augmented alcohol-cue reactivity. Memory inhibition (MI), the ability to voluntarily suppress unwanted thoughts/memories, may lead to forgetting of memories in several psychiatric conditions. However, despite its potential clinical implications, no study to date has explored the MI abilities in populations with substance misuse, such as binge drinkers (BDs).
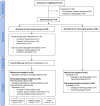
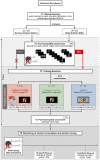
Method: This study-registered in the NIH Clinical Trials Database (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT05237414)-aims firstly to examine the behavioral and electroencephalographic (EEG) correlates of MI among college BDs. For this purpose, 45 BDs and 45 age-matched non/low-drinkers (50% female) will be assessed by EEG while performing the Think/No-Think Alcohol task, a paradigm that evaluates alcohol-related MI. Additionally, this work aims to evaluate an alcohol-specific MI intervention protocol using cognitive training (CT) and transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) while its effects on behavioral and EEG outcomes are assessed. BDs will be randomly assigned to one MI training group: combined [CT and verum tDCS applied over the right dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC)], cognitive (CT and sham tDCS), or control (sham CT and sham tDCS). Training will occur in three consecutive days, in three sessions. MI will be re-assessed in BDs through a post-training EEG assessment. Alcohol use and craving will be measured at the first EEG assessment, and both 10-days and 3-months post-training. In addition, behavioral and EEG data will be collected during the performance of an alcohol cue reactivity (ACR) task, which evaluates attentional bias toward alcoholic stimuli, before, and after the MI training sessions.
Discussion: This study protocol will provide the first behavioral and neurofunctional MI assessment in BDs. Along with poor MI abilities, BDs are expected to show alterations in event-related potentials and functional connectivity patterns associated with MI. Results should also demonstrate the effectiveness of the protocol, with BDs exhibiting an improved capacity to suppress alcohol-related memories after both combined and cognitive training, along with a reduction in alcohol use and craving in the short/medium-term. Collectively, these findings might have major implications for the understanding and treatment of alcohol misuse.
Clinical trial registration: [www.ClinicalTrials.gov], identifier [NCT05237414].
Keywords: alcohol; binge drinking; cognitive training; craving; electroencephalograpy (EEG); memory inhibition; randomized controlled trial; transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS).
Copyright © 2022 Almeida-Antunes, Vasconcelos, Crego, Rodrigues, Sampaio and López-Caneda.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

