Magnetic resonance imaging-guided radiotherapy for intermediate- and high-risk prostate cancer: Trade-off between planning target volume margin and online plan adaption
- PMID: 35844255
- PMCID: PMC9283928
- DOI: 10.1016/j.phro.2022.06.013
Magnetic resonance imaging-guided radiotherapy for intermediate- and high-risk prostate cancer: Trade-off between planning target volume margin and online plan adaption
Abstract
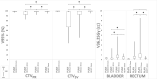
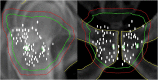
Magnetic resonance-guided radiotherapy with daily plan adaptation for intermediate- and high-risk prostate cancer is time and labor intensive. Fifty adapted plans with 3 mm planning target volume (PTV)-margin were compared with non-adapted plans using 3 or 5 mm margins. Adequate (V95% ≥ 95%) prostate coverage was achieved in 49 fractions with 5 mm PTV without plan adaptation, however, coverage of the seminal vesicles (SV) was insufficient in 15 of 50 fractions. There was no insufficient coverage for prostate and SV using plan adaptation with 3 mm. Hence, daily adaptation is recommended to obtain adequate SV-coverage when using 3 mm PTV.
Keywords: Dosimetry; Interfraction motion; MR-guided radiotherapy; Plan adaptation; Prostate cancer; Seminal vesicles.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Mottet N, Bellmunt J, Briers E, Bolla M, Bourke L, Cornford P, et al. EAU-ESTRO-ESUR-SIOG Guidelines on Prostate Cancer. Edn. presented at the EAU Annual Congress Amsterdam 2020. 978-94-92671-07-3. Publisher: EAU Guidelines Office. Place published: Arnhem, The Netherlands. https://uroweb.org/guideline/prostate-cancer/.
-
- Nakamura K., Mizowaki T., Inokuchi H., Ikeda I., Inoue T., Kamba T., et al. Decreased acute toxicities of intensity-modulated radiation therapy for localized prostate cancer with prostate-based versus bone-based image guidance. Int J Clin Oncol. 2018;23:158–164. doi: 10.1007/s10147-017-1174-2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rosario T., van der Weide L., Admiraal M., Piet M., Slotman B., Cuijpers J. Toward planning target volume margin reduction for the prostate using intrafraction motion correction with online kV imaging and automatic detection of implanted gold seeds. Pract Radiat Oncol. 2018;8(6):422–428. doi: 10.1016/j.prro.2018.04.008. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

