Alterations in biogenic amines levels associated with age-related muscular tissue impairment in Drosophila melanogaster
- PMID: 35844402
- PMCID: PMC9280237
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2022.03.006
Alterations in biogenic amines levels associated with age-related muscular tissue impairment in Drosophila melanogaster
Abstract
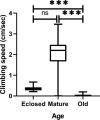
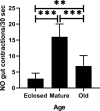
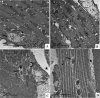
While holding on youth may be a universal wish, aging is a natural process associated with physical and physiological impairment in living organisms. Drosophila provides useful insights into aging-related events. Hence, this study was conducted to investigate the age-related changes in muscle function and architecture in relation to the biogenic amine titers. To achieve this aim, visceral and skeletal muscles performance was tested in newly-eclosed, sexually mature and old adult flies using climbing and gut motility assays. In addition, age-related ultrastructural alterations of muscular tissue were observed using transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The titer of selected biogenic amines was measured using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The results demonstrated that old flies were dramatically slower in upward movement than either newly-eclosed or sexually mature flies. Similarly, gut contraction rate was significantly lower in old flies than the sexually mature, although it was markedly higher than that in the newly-eclosed flies. In TEM examination, there were several ultrastructural changes in the midgut epithelium, legs and thorax muscles of old flies. Regarding biogenic amine titers, the old flies had significantly lower concentrations of octopamine, dopamine and serotonin than the sexually mature. We concluded that aging has adverse effects on muscular system function and ultrastructure, synchronized with biogenic amine titers changes. Our results highlighted the need for more researches on therapeutics that may balance the levels of age-related alterations in biogenic amines.
Keywords: Aging; Biogenic amines; Drosophila; Muscles; TEM.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures





References
-
- Adams M.D., Celniker S.E., Holt R.A., Evans C.A., Gocayne J.D., Amanatides P.G., Scherer S.E., Li P.W., Hoskins R.A., Galle R.F. The genome sequence of Drosophila melanogaster. Science. 2000;287:2185–2195. - PubMed
-
- Anton-Erxleben F., Miquel J., Philpott D.E. Fine-structural changes in the midgut of old Drosophila melanogaster. Mech. Aging Dev. 1983;23(3–4):265–276. - PubMed
-
- Balfanz S., Strünker T., Frings S., Baumann A. A family of octapamine receptors that specifically induce cyclic amp production or ca2+ release in Drosophila melanogaster. J. Neurochem. 2005;93:440–451. - PubMed
-
- Barbeau H., Rossignol S. Initiation and modulation of the locomotor pattern in the adult chronic spinal cat by noradrenergic, serotonergic and dopaminergic drugs. Brain Res. 1991;546(2):250–260. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

