Protective effect of Apremilast against LPS-induced acute lung injury via modulation of oxidative stress and inflammation
- PMID: 35844406
- PMCID: PMC9280219
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2022.02.023
Protective effect of Apremilast against LPS-induced acute lung injury via modulation of oxidative stress and inflammation
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "Protective effect of Apremilast against LPS-induced acute lung injury via modulation of oxidative stress and inflammation" [Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 29(5) (2022) 3414-3424].Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022 Jun;29(6):103279. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2022.103279. Epub 2022 Apr 13. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35503423 Free PMC article.
Abstract
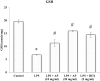
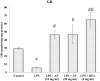
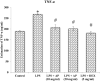
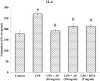
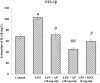
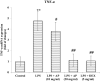
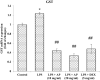
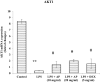
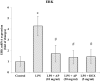
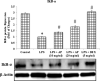
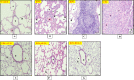
Lung injuries are attributed due to exposure to Drugs or chemicals. One of the important challenging situations for the clinicians is to manage treatments of different diseases with acute lung injury (ALI). The objective of this study was to investigate the possible protective mechanisms and action of a novel Phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor "Apremilast" (AP) in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced lung injury. Blood sample from each animals were collected in a vacuum blood collection tube. The rat lungs were isolated for oxidative stress assessment, western blot analysis and their mRNA expressions using RT-PCR. Exposure of LPS in rats causes significant increase in oxidative stress, activates the pro-inflammatory cytokines release like tissue necrotic factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and interleukin-6 (IL-6), modulated gene expression, protein expression and histopathological changes which were reversed by administration of AP. Finding of the research enlighten the protective role of AP against LPS-induced ALI.
Keywords: Acute lung injury; Apremilast; Lipopolysaccharides; Oxidative stress; mRNA expressions.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effect of Apremilast on LPS-induced immunomodulation and inflammation via activation of Nrf2/HO-1 pathways in rat lungs.Saudi Pharm J. 2023 Jul;31(7):1327-1338. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2023.05.022. Epub 2023 May 29. Saudi Pharm J. 2023. PMID: 37323920 Free PMC article.
-
Kegan Liyan oral liquid ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury through inhibition of TLR4-mediated NF-κB signaling pathway and MMP-9 expression.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Jun 20;186:91-102. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.03.057. Epub 2016 Mar 30. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27036629
-
JFNE-A isolated from Jing-Fang n-butanol extract attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting oxidative stress and the NF-κB signaling pathway via promotion of autophagy.Phytomedicine. 2022 Feb;96:153891. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153891. Epub 2021 Dec 20. Phytomedicine. 2022. PMID: 35026506
-
Qingwenzhike Prescription Alleviates Acute Lung Injury Induced by LPS via Inhibiting TLR4/NF-kB Pathway and NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Dec 23;12:790072. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.790072. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 35002723 Free PMC article.
-
Blocking of tripartite motif 8 protects against lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced acute lung injury by regulating AMPKα activity.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019 Jan 15;508(3):701-708. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.11.072. Epub 2018 Dec 5. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019. PMID: 30527811
References
-
- Al-Harbi N.O., Imam F., Alharbi M.M., Khan M.R., Qamar W., Afzal M., Algahtani M., Alobaid S., Alfardan A.S., Alshammari A., Albekairi T.H., Alharbi K.S. Role of rivaroxaban in sunitinib-induced renal injuries via inhibition of oxidative stress-induced apoptosis and inflammation through the tissue nacrosis factor-α induced nuclear factor-κappa B signaling pathway in rats. J. Thromb. Thrombol. 2020;50(2):361–370. - PubMed
-
- Avecillas J.F., Freire A.X., Arroliga A.C. Clinical epidemiology of acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome: incidence, diagnosis, and outcomes. Clin. Chest Med. 2006;27(4):549–557. abstract vii. - PubMed
-
- Boje K.M. Nitric oxide neurotoxicity in neurodegenerative diseases. Front. Biosci. 2004;9:763–776. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

