Effects of Different Types of Early Restrictive Fluid Resuscitation on Immune Function and Multiorgan Damage on Hemorrhagic Shock Rat Model in a Hypothermic Environment
- PMID: 35844441
- PMCID: PMC9279086
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/4982047
Effects of Different Types of Early Restrictive Fluid Resuscitation on Immune Function and Multiorgan Damage on Hemorrhagic Shock Rat Model in a Hypothermic Environment
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Effects of Different Types of Early Restrictive Fluid Resuscitation on Immune Function and Multiorgan Damage on Hemorrhagic Shock Rat Model in a Hypothermic Environment.Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Jun 28;2023:9807657. doi: 10.1155/2023/9807657. eCollection 2023. Comput Math Methods Med. 2023. PMID: 37416225 Free PMC article.
Abstract
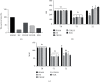
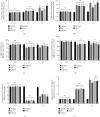
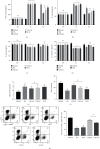
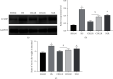
Objective: This study was aimed at investigating the effects of different types of fluid restriction fluid resuscitation on the immune dysfunction and organ injury of hemorrhagic shock rats under a hypothermic environment.
Methods: SD rats were divided into sham operation group (SHAM), hemorrhagic shock model group (HS), crystal liquid limited resuscitation group (CRLLR), colloidal liquid limited resuscitation group (COLLR), and nonlimited resuscitation group (NLR); rats in each group were placed in a low-temperature environment of 0-5°C for 30 min, and then, a hemorrhagic shock rat model was prepared. Sodium lactate Ringer's restricted resuscitation solution, hydroxyethyl starch restricted resuscitation solution, and hydroxyethyl starch were used for resuscitation, and hemodynamic examination was performed. The mortality rate, inflammatory factors, oxidative stress factors, and immune function were detected by ELISA. The dysfunction and injury of the intestinal, lung, liver, and kidney were examined by histological methods.
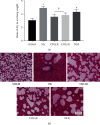
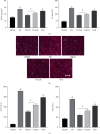
Results: Hemorrhagic shock resulted in decreased immune function and activation of inflammation. Unrestricted fluid infusion further activated the inflammatory response. The crystalloid-restricted fluid infusion performed effectively to regulate inflammatory response, promote antioxidative activity, and reduce the immunosuppressive reaction. Rehydration could regulate the coagulation. The hydroxyethyl starch reduced the expression of platelet glycoproteins Ib and IIb/IIIa and blocked the binding of fibrinogen to activated platelets, thereby inhibiting intrinsic coagulation and platelet adhesion and aggregation. Rats in the CRLLR group showed to relieve the injury of the lung, liver, kidney, and intestine from hemorrhagic shock in low-temperature environment.
Conclusion: The early application of restrictive crystalloid resuscitation in hemorrhagic shock rats in hypothermic environment showed the best therapy results. Early LR-restrictive fluid replacement promotes the balance of inflammatory response and the recovery of immunosuppressive state, resists oxidative stress, stabilizes the balance of coagulation and fibrinolysis, improves coagulation function, and relieves organ injury.
Copyright © 2022 Linlin Xu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

