Clinical Application of Remifentanil Combined with Sevoflurane in Manual Reduction of Humeral Supracondylar Fracture in Children
- PMID: 35844458
- PMCID: PMC9286932
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/2410433
Clinical Application of Remifentanil Combined with Sevoflurane in Manual Reduction of Humeral Supracondylar Fracture in Children
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Clinical Application of Remifentanil Combined with Sevoflurane in Manual Reduction of Humeral Supracondylar Fracture in Children.Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Sep 27;2023:9789628. doi: 10.1155/2023/9789628. eCollection 2023. Comput Math Methods Med. 2023. PMID: 37811281 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Objective: To explore the effect of the combination of remifentanil and sevoflurane on children with humeral supracondylar fractures undergoing manual reduction.
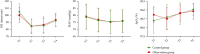
Methods: A total of 60 children undergoing manual reduction external fixation due to humeral supracondylar fractures were enrolled between September 2020 and September 2021. According to the random number table method, they were divided into the control group (inhalation of 7% sevoflurane) and the observation group (inhalation of 7% sevoflurane and intravenous infusion of remifentanil). The heart rate (HR), mean arterial pressure (MAP), and blood oxygen saturation (SpO2) in both groups were investigated. The sedation and analgesic effects, fracture reduction, and complications were compared between the two groups.
Results: There was no significant difference found in HR, MAP, or SpO2 between the two groups at 3 minutes prior to anesthesia, 2 minutes post anesthesia, and post manual reduction (P > 0.05). The difference in HR, MAP, and SpO2 between the two groups was not statistically significant at any time point (P > 0.05). The good rate of sedation and analgesia in the observation group was 93.33%, which is significantly higher than that in the control group (P < 0.05). The reduction time and success rate of one-time manual reduction in the observation group were higher than those in the control group (P < 0.05). There was no significant difference in fracture healing time between the two groups (P > 0.05). Both groups had airway complications (nausea and vomiting, neurovascular damage and asphyxia, and laryngospasm).
Conclusion: The combination of remifentanil and sevoflurane showed good sedative and analgesic effects on children with humeral supracondylar fractures undergoing manual reduction with relatively higher safety.
Copyright © 2022 Youqing Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Jinyu Y. Anesthesia effect of dexmedetomidine and midazolam on orthopedic surgery for children with congenital digital deformity under brachial plexus anesthesia. Chinese Journal of Medicine and Clinical Medicine . 2019;19(16):2803–2804.
-
- Sousa-Júnior F. A., Souza A. S. R., Lima L. C., et al. Intraoperative clonidine to prevent postoperative emergence delirium following sevoflurane anesthesia in pediatric patients: a randomized clinical trial. Brazilian Journal of Anesthesiology . 2021;71(1):5–10. doi: 10.1016/j.bjane.2020.12.003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jian S. Effect of anesthesia on functional recovery of children with supracondylar humerus fracture surgery. PLA Journal of Preventive Medicine . 2019;37(7):89–91.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources