Digesting the Role of JAK-STAT and Cytokine Signaling in Oral and Gastric Cancers
- PMID: 35844493
- PMCID: PMC9277720
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.835997
Digesting the Role of JAK-STAT and Cytokine Signaling in Oral and Gastric Cancers
Abstract
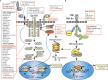
When small proteins such as cytokines bind to their associated receptors on the plasma membrane, they can activate multiple internal signaling cascades allowing information from one cell to affect another. Frequently the signaling cascade leads to a change in gene expression that can affect cell functions such as proliferation, differentiation and homeostasis. The Janus kinase-signal transducer and activator of transcription (JAK-STAT) and the tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR) are the pivotal mechanisms employed for such communication. When deregulated, the JAK-STAT and the TNF receptor signaling pathways can induce chronic inflammatory phenotypes by promoting more cytokine production. Furthermore, these signaling pathways can promote replication, survival and metastasis of cancer cells. This review will summarize the essentials of the JAK/STAT and TNF signaling pathways and their regulation and the molecular mechanisms that lead to the dysregulation of the JAK-STAT pathway. The consequences of dysregulation, as ascertained from founding work in haematopoietic malignancies to more recent research in solid oral-gastrointestinal cancers, will also be discussed. Finally, this review will highlight the development and future of therapeutic applications which modulate the JAK-STAT or the TNF signaling pathways in cancers.
Keywords: JAK; PROTAC (proteolysis-targeting chimeric molecule); STAT; TNF; cancer; cytokines; gastric; oral.
Copyright © 2022 Ni, Low, Silke and O’Reilly.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signal transduction and the Janus Kinase/Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription (JAK-STAT) pathway.Biofactors. 2009 Jan-Feb;35(1):76-81. doi: 10.1002/biof.20. Biofactors. 2009. PMID: 19319849 Review.
-
[Research Advances of JAK/STAT Signaling Pathway in Lung Cancer].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2019 Jan 20;22(1):45-51. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2019.01.09. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 30674393 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
The JAK/STAT signaling cascade in gastric carcinoma (Review).Int J Oncol. 2015 Nov;47(5):1617-26. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2015.3160. Epub 2015 Sep 14. Int J Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26398764 Review.
-
Malignant JAK-signaling: at the interface of inflammation and malignant transformation.Leukemia. 2025 May;39(5):1011-1030. doi: 10.1038/s41375-025-02569-8. Epub 2025 Mar 26. Leukemia. 2025. PMID: 40140631 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drosophila Jak/STAT Signaling: Regulation and Relevance in Human Cancer and Metastasis.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Dec 14;19(12):4056. doi: 10.3390/ijms19124056. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30558204 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CTGF, FN1, IL-6, THBS1, and WISP1 genes and PI3K-Akt signaling pathway as prognostic and therapeutic targets in gastric cancer identified by gene network modeling.Discov Oncol. 2024 Aug 12;15(1):344. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01225-4. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39133458 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Inflammation-Associated Factors in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.J Inflamm Res. 2023 Sep 27;16:4301-4315. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S428358. eCollection 2023. J Inflamm Res. 2023. PMID: 37791117 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wogonin suppresses proliferation, invasion and migration in gastric cancer cells via targeting the JAK-STAT3 pathway.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 28;14(1):30803. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-81196-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39730467 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic development and validation of a prediction model based on major histocompatibility complex-related differentially expressed genes in stomach adenocarcinoma.Transl Cancer Res. 2025 Jan 31;14(1):33-61. doi: 10.21037/tcr-24-707. Epub 2025 Jan 21. Transl Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 39974425 Free PMC article.
-
The chemopreventive effects of native Brazilian plants on stomach cancer: A review of the last 25 years.Oncoscience. 2025 May 8;12:36-51. doi: 10.18632/oncoscience.618. eCollection 2025. Oncoscience. 2025. PMID: 40343252 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

