Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Score Analysis for Predicting the Expression of the Immunotherapy Biomarker PD-L1 in Lung Cancer
- PMID: 35844508
- PMCID: PMC9286729
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.893198
Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Score Analysis for Predicting the Expression of the Immunotherapy Biomarker PD-L1 in Lung Cancer
Abstract
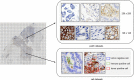
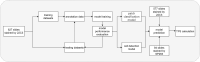
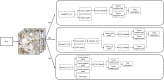
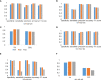
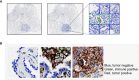
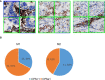
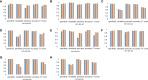
Programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) is a critical biomarker for predicting the response to immunotherapy. However, traditional quantitative evaluation of PD-L1 expression using immunohistochemistry staining remains challenging for pathologists. Here we developed a deep learning (DL)-based artificial intelligence (AI) model to automatically analyze the immunohistochemical expression of PD-L1 in lung cancer patients. A total of 1,288 patients with lung cancer were included in the study. The diagnostic ability of three different AI models (M1, M2, and M3) was assessed in both PD-L1 (22C3) and PD-L1 (SP263) assays. M2 and M3 showed improved performance in the evaluation of PD-L1 expression in the PD-L1 (22C3) assay, especially at 1% cutoff. Highly accurate performance in the PD-L1 (SP263) was also achieved, with accuracy and specificity of 96.4 and 96.8% in both M2 and M3, respectively. Moreover, the diagnostic results of these three AI-assisted models were highly consistent with those from the pathologist. Similar performances of M1, M2, and M3 in the 22C3 dataset were also obtained in lung adenocarcinoma and lung squamous cell carcinoma in both sampling methods. In conclusion, these results suggest that AI-assisted diagnostic models in PD-L1 expression are a promising tool for improving the efficiency of clinical pathologists.
Keywords: AI; NSCLC; PD-L1; automated scoring; pathological diagnosis.
Copyright © 2022 Cheng, Zhang, Xing, Hu, Zhang, Chen, Li, Peng, Ding, Zhang, Chen, Xia and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
FZ, YX, SC, ML, PC, DZ and CP are current or former employees of the company 3D Medicines Inc. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Incorvaia L, Fanale D, Badalamenti G, Barraco N, Bono M, Corsini LR, et al. Programmed Death Ligand 1 (PD-L1) as a Predictive Biomarker for Pembrolizumab Therapy in Patients With Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). Adv Ther (2019) 36(10):2600–17. doi: 10.1007/s12325-019-01057-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

