Extracellular CIRP Promotes GPX4-Mediated Ferroptosis in Sepsis
- PMID: 35844517
- PMCID: PMC9277504
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.903859
Extracellular CIRP Promotes GPX4-Mediated Ferroptosis in Sepsis
Abstract
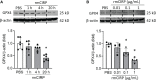
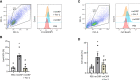
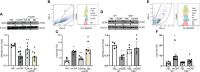
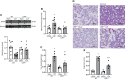
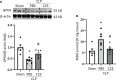
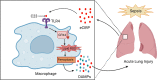
Sepsis is characterized by life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated host response to infection. Extracellular cold-inducible RNA-binding protein (eCIRP) is a damage-associated molecular pattern (DAMP) that promotes inflammation and induces cell death via apoptosis, NETosis, and/or pyroptosis. Ferroptosis is a form of regulated cell death characterized by the accumulation of lipid peroxide on cellular membranes. We hypothesize that eCIRP induces ferroptosis in macrophages and lung tissue during sepsis. RAW 264.7 cells stimulated with recombinant murine (rm) CIRP significantly decreased the expression of glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4), a negative regulator of ferroptosis, and increased lipid reactive oxygen species (ROS) in a TLR4 dependent manner. In TLR4-/- peritoneal macrophages, depression of GPX4 expression and increase in lipid ROS levels were attenuated after rmCIRP-treatment compared to WT macrophages. rmCIRP also induced cell death in RAW 264.7 cells which was corrected by the ferroptosis inhibitor, ferrostatin-1 (Fer-1). Intraperitoneal injection of rmCIRP decreased GPX4 expression and increased lipid ROS in lung tissue, whereas the increase of lipid ROS was reduced by Fer-1 treatment. GPX4 expression was significantly decreased, while malondialdehyde (MDA), iron levels, and injury scores were significantly increased in lungs of WT mice after cecal ligation and puncture (CLP)-induced sepsis compared to CIRP-/- mice. Treatment with C23, a specific eCIRP inhibitor, in CLP mice alleviated the decrease in GPX4 and increase in MDA levels of lung tissue. These findings suggest that eCIRP induces ferroptosis in septic lungs by decreasing GPX4 and increasing lipid ROS. Therefore, regulation of ferroptosis by targeting eCIRP may provide a new therapeutic approach in sepsis and other inflammatory diseases.
Keywords: GPX4; acute lung injury; eCIRP; ferroptosis; lung; macrophage; sepsis.
Copyright © 2022 Shimizu, Murao, Nofi, Wang and Aziz.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Extracellular CIRP decreases Siglec-G expression on B-1a cells skewing them towards a pro-inflammatory phenotype in sepsis.Mol Med. 2021 May 31;27(1):55. doi: 10.1186/s10020-021-00318-y. Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34058975 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular CIRP promotes Kupffer cell inflammatory polarization in sepsis.Front Immunol. 2024 May 30;15:1411930. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1411930. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38881891 Free PMC article.
-
Nicotinamide mononucleotide mitigates hyperoxia-aggravated septic lung injury via the GPx4-mediated anti-ferroptosis signaling pathway in alveolar epithelial cells.Free Radic Biol Med. 2025 Jul;234:86-99. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2025.04.021. Epub 2025 Apr 15. Free Radic Biol Med. 2025. PMID: 40246251
-
Extracellular CIRP (eCIRP) and inflammation.J Leukoc Biol. 2019 Jul;106(1):133-146. doi: 10.1002/JLB.3MIR1118-443R. Epub 2019 Jan 15. J Leukoc Biol. 2019. PMID: 30645013 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GPX4 at the Crossroads of Lipid Homeostasis and Ferroptosis.Proteomics. 2019 Sep;19(18):e1800311. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201800311. Epub 2019 May 31. Proteomics. 2019. PMID: 30888116 Review.
Cited by
-
The Ferroptosis-Mitochondrial Axis in Depression: Unraveling the Feedforward Loop of Oxidative Stress, Metabolic Homeostasis Dysregulation, and Neuroinflammation.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 May 20;14(5):613. doi: 10.3390/antiox14050613. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40427494 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The mechanism of ferroptosis and its related diseases.Mol Biomed. 2023 Oct 16;4(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s43556-023-00142-2. Mol Biomed. 2023. PMID: 37840106 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interaction between macrophages and ferroptosis: Metabolism, function, and diseases.Chin Med J (Engl). 2025 Mar 5;138(5):509-522. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000003189. Epub 2024 Sep 6. Chin Med J (Engl). 2025. PMID: 39245648 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DAMPs and radiation injury.Front Immunol. 2024 Jan 25;15:1353990. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1353990. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38333215 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal stem cells alleviate sepsis-induced acute lung injury by blocking neutrophil extracellular traps formation and inhibiting ferroptosis in rats.PeerJ. 2024 Jan 29;12:e16748. doi: 10.7717/peerj.16748. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 38304189 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rudd KE, Johnson SC, Agesa KM, Shackelford KA, Tsoi D, Kievlan DR, et al. . Global, Regional, and National Sepsis Incidence and Mortality, 1990-2017: Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet (London England) (2020) 395(10219):200–11. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32989-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

