Identification of Critical Biomarkers and Immune Infiltration in Rheumatoid Arthritis Based on WGCNA and LASSO Algorithm
- PMID: 35844557
- PMCID: PMC9277141
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.925695
Identification of Critical Biomarkers and Immune Infiltration in Rheumatoid Arthritis Based on WGCNA and LASSO Algorithm
Abstract
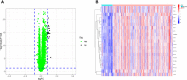
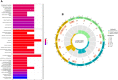
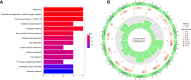
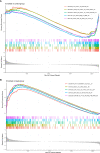
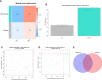
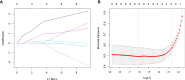
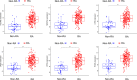
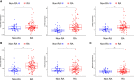
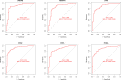
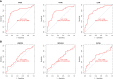
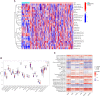
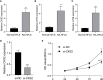
Rheumatoid arthritis(RA) is the most common inflammatory arthritis, and a significant cause of morbidity and mortality. RA patients' synovial inflammation contains a variety of genes and signalling pathways that are poorly understood. It was the goal of this research to discover the major biomarkers related to the course of RA and how they connect to immune cell infiltration. The Gene Expression Omnibus was used to download gene microarray data. Differential expression analysis, weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA), and least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression were used to identify hub markers for RA. Single-sample GSEA was used to examine the infiltration levels of 28 immune cells and their connection to hub gene markers. The hub genes' expression in RA-HFLS and HFLS cells was verified by RT-PCR. The CCK-8 assay was applied to determine the roles of hub genes in RA. In this study, we identified 21 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in RA. WGCNA yielded two co-expression modules, one of which exhibited the strongest connection with RA. Using a combination of differential genes, a total of 6 intersecting genes was discovered. Six hub genes were identified as possible biomarkers for RA after a lasso analysis was performed on the data. Three hub genes, CKS2, CSTA, and LY96, were found to have high diagnostic value using ROC curve analysis. They were shown to be closely related to the concentrations of several immune cells. RT-PCR confirmed that the expressions of CKS2, CSTA and LY96 were distinctly upregulated in RA-HFLS cells compared with HFLS cells. More importantly, knockdown of CKS2 suppressed the proliferation of RA-HFLS cells. Overall, to help diagnose and treat RA, it's expected that CKS2, CSTA, and LY96 will be available, and the aforementioned infiltration of immune cells may have a significant impact on the onset and progression of the disease.
Keywords: GEO datasets; diagnostic marker; immune cells infiltration; machinelearning; rheumatoid arthritis.
Copyright © 2022 Jiang, Zhou and Shen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

