The Non-Receptor Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase PTPN6 Mediates a Positive Regulatory Approach From the Interferon Regulatory Factor to the JAK/STAT Pathway in Litopenaeus vannamei
- PMID: 35844582
- PMCID: PMC9276969
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.913955
The Non-Receptor Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase PTPN6 Mediates a Positive Regulatory Approach From the Interferon Regulatory Factor to the JAK/STAT Pathway in Litopenaeus vannamei
Abstract
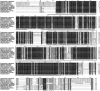
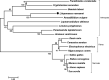
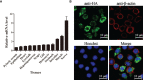
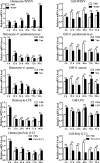
SH2-domain-containing protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTPs), belonging to the class I PTP superfamily, are responsible for the dephosphorylation on the phosphorylated tyrosine residues in some proteins that are involved in multiple biological processes in eukaryotes. The Janus kinase/signal transducers and activators of transcription (JAK/STAT) pathway transduce signaling responding to interferons and initiate cellular antiviral responses. The activity of the JAK/STAT pathway is generally orchestrated by the de-/phosphorylation of the tyrosine and serine residues of JAKs and STATs, in which the dephosphorylation processes are mainly controlled by PTPs. In the present study, an SH2-domian-contianing PTP, temporally named as LvPTPN6, was identified in Litopenaeus vannamei. LvPTPN6 shares high similarity with PTPN6s from other organisms and was phylogenetically categorized into the clade of arthropods that differs from those of fishes and mammals. LvPTPN6 was constitutively expressed in all detected tissues, located mainly in the cytoplasm, and differentially induced in hemocyte and gill after the challenge of stimulants, indicating its complicated regulatory roles in shrimp immune responses. Intriguingly, the expression of LvPTPN6 was regulated by interferon regulatory factor (IRF), which could directly bind to the LvPTPN6 promoter. Surprisingly, unlike other PTPN6s, LvPTPN6 could promote the dimerization of STAT and facilitate its nuclear localization, which further elevated the expression of STAT-targeting immune effector genes and enhanced the antiviral immunity of shrimp. Therefore, this study suggests a PTPN6-mediated regulatory approach from IRF to the JAK/STAT signaling pathway in shrimp, which provides new insights into the regulatory roles of PTPs in the JAK/STAT signaling pathway and contributes to the further understanding of the mechanisms of antiviral immunity in invertebrates.
Keywords: IFN regulatory factor; JAK/STAT signaling pathway; Litopenaeus vannamei; antiviral immunity; non-receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase.
Copyright © 2022 Luo, Xu, Liu, Shen, Yang, Zhu, Weng, He and Zuo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
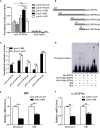

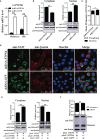
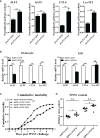
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

