How to Maintain a Sustainable Doctor-Patient Relationship in Healthcare in China: A Structural Equation Modeling Approach
- PMID: 35844669
- PMCID: PMC9277155
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/8251220
How to Maintain a Sustainable Doctor-Patient Relationship in Healthcare in China: A Structural Equation Modeling Approach
Abstract
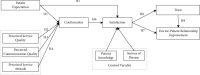
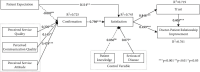
It is important to identify means of improving and maintaining a sustainable doctor-patient relationship to address current healthcare issues. Although many studies have made outstanding contributions to the healthcare doctor-patient relationship literature, little work has been done to explore the influencing elements of the doctor-patient relationship in relation to expectation confirmation theory. To fill this gap, this study produced a theoretical framework model of the influencing factors of the doctor-patient relationship according to the expectation confirmation theory. Data from 335 Chinese patients were analyzed using a structural equation modeling method, and the results showed that patient satisfaction and patient trust are the most important factors in building a good relationship between doctor and patient. Furthermore, three components of postdiagnosis patient's perception, namely, perceived service quality, perceived communication quality, and perceived service attitude, are examined. These have a significant impact on patient confirmation. These three components ultimately affect the doctor-patient relationship. This study will be helpful for doctors to understand patients' service demands and their future diagnosis behavior. The proposals of this study may lead to optimization of the process of diagnosis and improvements in the quality of clinic services.
Copyright © 2022 Zhan-You Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rebuild doctor-patient trust in medical service delivery in China.Sci Rep. 2020 Dec 15;10(1):21956. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-78921-y. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33319841 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Screen-to-Screen Versus Face-to-Face Consultation on Doctor-Patient Communication: An Experimental Study with Simulated Patients.J Med Internet Res. 2017 Dec 20;19(12):e421. doi: 10.2196/jmir.8033. J Med Internet Res. 2017. PMID: 29263017 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of contract service policy and doctor communication skills on rural patient-doctor trust relationship in the village clinics of three counties.BMC Health Serv Res. 2019 Mar 22;19(1):187. doi: 10.1186/s12913-019-3875-x. BMC Health Serv Res. 2019. PMID: 30902058 Free PMC article.
-
[Doctor-patient relationship--its quality and possibilities for improvement].Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1992 Mar 28;122(13):475-80. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1992. PMID: 1566017 Review. German.
-
[Changing patients' health behavior--consultation and physician-patient relationship].Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen. 1993 Jan 10;113(1):47-50. Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen. 1993. PMID: 8424251 Review. Norwegian.
Cited by
-
Medical service quality evaluation based on LDA and sentiment analysis: Examples of seven chronic diseases.Digit Health. 2024 Mar 6;10:20552076241233864. doi: 10.1177/20552076241233864. eCollection 2024 Jan-Dec. Digit Health. 2024. PMID: 38465296 Free PMC article.
-
How the use of an online healthcare community affects the doctor-patient relationship: An empirical study in China.Front Public Health. 2023 Apr 6;11:1145749. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1145749. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37089478 Free PMC article.
-
Research on collaborative development mechanism of multiple stakeholders in medical institutions based on rough set.BMC Public Health. 2024 Feb 6;24(1):387. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-17813-6. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38321441 Free PMC article.
-
Factors associated with patient-physician relationships: perspectives of medical personnel in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China.BMC Health Serv Res. 2025 Mar 6;25(1):349. doi: 10.1186/s12913-025-12475-5. BMC Health Serv Res. 2025. PMID: 40050825 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hussain A., Sial M., Usman S., Hwang J., Jiang Y., Shafiq A. What factors affect patient satisfaction in public sector hospitals: evidence from an emerging economy. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health . 2019;16(6):p. 994. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16060994. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Liang C., Gu D., Tao F., Jain H. K., Zhao Y., Ding B. Influence of mechanism of patient-accessible hospital information system implementation on doctor-patient relationships: a service fairness perspective. Information & Management . 2017;54(1):57–72. doi: 10.1016/j.im.2016.03.010. - DOI
-
- Gong X., Zhang J., Siddiqui M. M. Effects of medical security satisfaction and trust in doctors on subjective well-being: evidence from China. International Journal of Management and Sustainability . 2019;8(3):133–150. doi: 10.18488/journal.11.2019.83.133.150. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous