Modeling of the Small-Scale Outbreak of COVID-19
- PMID: 35844852
- PMCID: PMC9283974
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.907814
Modeling of the Small-Scale Outbreak of COVID-19
Abstract
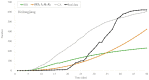
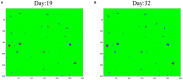
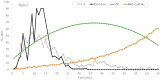
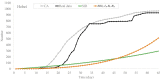
With the improvement of treatment and prevention methods, many countries have the pandemic under control. Different from the globally large-scale outbreak of COVID-19 in 2020, now the outbreak in these countries shows new characteristics, which calls for an effective epidemic model to describe the transmission dynamics. Meeting this need, first, we extensively investigate the small-scale outbreaks in different provinces of China and use classic compartmental models, which have been widely used in predictions, to forecast the outbreaks. Additionally, we further propose a new version of cellular automata with a time matrix, to simulate outbreaks. Finally, the experimental results show that the proposed cellular automata could effectively simulate the small-scale outbreak of COVID-19, which provides insights into the transmission dynamics of COVID-19 in China and help countries with small-scale outbreaks to determine and implement effective intervention measures. The countries with relatively small populations will also get useful information about the epidemic from our research.
Keywords: COVID-19; cellular automata; simulation; small-scale outbreak; time matrix.
Copyright © 2022 Wu, Zhang and Zhao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A COVID-19 Pandemic Artificial Intelligence-Based System With Deep Learning Forecasting and Automatic Statistical Data Acquisition: Development and Implementation Study.J Med Internet Res. 2021 May 20;23(5):e27806. doi: 10.2196/27806. J Med Internet Res. 2021. PMID: 33900932 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling of the Long-Term Epidemic Dynamics of COVID-19 in the United States.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Jul 16;18(14):7594. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18147594. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34300045 Free PMC article.
-
Fleeing lockdown and its impact on the size of epidemic outbreaks in the source and target regions - a COVID-19 lesson.Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 29;11(1):9233. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-88204-9. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33927224 Free PMC article.
-
Outbreak of COVID-19: A Detailed Overview and Its Consequences.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1353:23-45. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-85113-2_2. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 35137366 Review.
-
Three phases of COVID-19: theoretical thinking on epidemic prevention and control.Ann Palliat Med. 2021 Jul;10(7):8271-8275. doi: 10.21037/apm-21-1582. Ann Palliat Med. 2021. PMID: 34353108 Review.
Cited by
-
Using the SEIQR model with epidemic amplifier effect to predict the final outbreak size of the COVID-19 in Dalian, Liaoning province, China.PLoS One. 2024 Dec 12;19(12):e0307239. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0307239. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39666686 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pandey G, Chaudhary P, Gupta R, Pal S. SEIR and Regression Model based COVID-19 outbreak predictions in India. arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.00958. (2020). 10.2196/preprints.19406 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

