Transoral incisionless fundoplication is cost-effective for treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease
- PMID: 35845021
- PMCID: PMC9286770
- DOI: 10.1055/a-1783-9378
Transoral incisionless fundoplication is cost-effective for treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease
Abstract
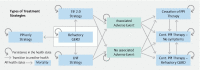
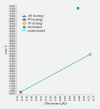
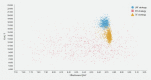
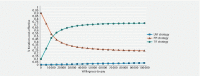
Background and study aims Given the sizable number of patients with symptomatic gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) despite proton pump inhibitor (PPI) therapy, non-pharmacologic treatment has become increasingly utilized. The aim of this study was to analyze the cost-effectiveness of medical, endoscopic, and surgical treatment of GERD. Patients and methods A deterministic Markov cohort model was constructed from the US healthcare payer's perspective to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of three competing strategies: 1) omeprazole 20 mg twice daily; 2) transoral incisionless fundoplication (TIF 2.0); and 3) laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication [LNF]. Cost was reported in US dollars with health outcomes recorded in quality-adjusted life years (QALYs). Ten-year and lifetime time horizons were utilized with 3 % discount rate and half-cycle corrections applied. The main outcome was incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) with a willingness-to-pay threshold of $ 100,000 per QALY. Probabilistic sensitivity analyses were also performed. Results In our base-case analysis, the average cost of TIF 2.0 was $ 13,978.63 versus $ 17,658.47 for LNF and $ 10,931.49 for PPI. Compared to the PPI strategy, TIF 2.0 was cost-effective with an incremental cost of $ 3,047 and incremental effectiveness of 0.29 QALYs, resulting in an ICER of $ 10,423.17 /QALY gained. LNF was strongly dominated by TIF 2.0. Over a lifetime horizon, TIF 2.0 remained the cost-effective strategy for patients with symptoms despite twice-daily 20-mg omeprazole. TIF 2.0 remained cost-effective after varying parameter inputs in deterministic and probabilistic sensitivity analyses and for scenario analyses in multiple age groups. Conclusions Based upon this study, TIF 2.0 was cost-effective for patients with symptomatic GERD despite low-dose, twice-daily PPI.
The Author(s). This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonDerivative-NonCommercial License, permitting copying and reproduction so long as the original work is given appropriate credit. Contents may not be used for commercial purposes, or adapted, remixed, transformed or built upon. (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests Thomas R. McCarty has no conflicts to disclose. Pichamol Jirapinyo has the following disclosures: Apollo Endosurgery – Research Support, Fractyl – Research Support, GI Dynamics – Research Support, Endogastric Solutions – Consultant. Lyndon P. James has no conflicts to disclose. Sanchit Gupta has no conflicts to disclose. Walter W. Chan has the following disclosures: Ironwood – scientific advisory board. Christopher C. Thompson has the following disclosures: Apollo Endosurgery – Consultant/Research Support (Consulting fees/Institutional Research Grants), Aspire Bariatrics – Research Support (Institutional Research Grant), BlueFlame Healthcare Venture Fund – General Partner, Boston Scientific – Consultant (Consulting fees), Covidien/Medtronic – Consultant (Consulting Fees), EnVision Endoscopy (Board Member), Fractyl – Consultant/Advisory Board Member (Consulting Fees), GI Dynamics – Consultant (Consulting Fees)/ Research Support (Institutional Research Grant), GI Windows – Ownership interest, Olympus/Spiration – Consultant (Consulting Fees)/Research Support (Equipment Loans), Spatz – Research Support (Institutional Research Grant), USGI Medical – Consultant (Consulting Fees)/Advisory Board Member (Consulting fees)/Research Support (Research Grant).
Figures
References
-
- Zagari R M, Fuccio L, Wallander M A et al.Gastro-oesophageal reflux symptoms, oesophagitis and Barrettʼs oesophagus in the general population: the Loiano-Monghidoro study. Gut. 2008;57:1354–1359. - PubMed
-
- Camilleri M, Dubois D, Coulie B et al.Prevalence and socioeconomic impact of upper gastrointestinal disorders in the United States: results of the US Upper Gastrointestinal Study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005;3:543–552. - PubMed
-
- Pace F, Bazzoli F, Fiocca R et al.The Italian validation of the Montreal Global definition and classification of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;21:394–408. - PubMed
-
- Vakil N, van Zanten S V, Kahrilas P.The Montreal definition and classification of gastroesophageal reflux disease: a global evidence-based consensus Am J Gastroenterol 20061011900–1920.; quiz 43 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

