Identification of Key Non-coding RNAs and Transcription Factors in Calcific Aortic Valve Disease
- PMID: 35845040
- PMCID: PMC9276990
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.826744
Identification of Key Non-coding RNAs and Transcription Factors in Calcific Aortic Valve Disease
Abstract
Background: Calcific aortic valve disease (CAVD) is one of the most frequently occurring valvular heart diseases among the aging population. Currently, there is no known pharmacological treatment available to delay or reverse CAVD progression. The regulation of gene expression could contribute to the initiation, progression, and treatment of CAVD. Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) and transcription factors play essential regulatory roles in gene expression in CAVD; thus, further research is urgently needed.
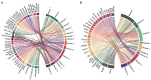
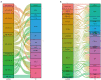
Materials and methods: The gene-expression profiles of GSE51472 and GSE12644 were obtained from the Gene Expression Omnibus database, and differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified in each dataset. A protein-protein-interaction (PPI) network of DEGs was then constructed using the Search Tool for the Retrieval of Interacting Genes/Proteins database, and functional modules were analyzed with ClusterOne plugin in Cytoscape. Furthermore, Gene Ontology-functional annotation and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes-pathway analysis were conducted for each functional module. Most crucially, ncRNAs and transcription factors acting on each functional module were separately identified using the RNAInter and TRRUST databases. The expression of predicted transcription factors and key genes was validated using GSE51472 and GSE12644. Furthermore, quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) experiments were performed to validate the differential expression of most promising candidates in human CAVD and control samples.
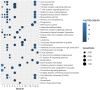
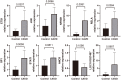
Results: Among 552 DEGs, 383 were upregulated and 169 were downregulated. In the PPI network, 15 functional modules involving 182 genes and proteins were identified. After hypergeometric testing, 45 ncRNAs and 33 transcription factors were obtained. Among the predicted transcription factors, CIITA, HIF1A, JUN, POU2F2, and STAT6 were differentially expressed in both the training and validation sets. In addition, we found that key genes, namely, CD2, CD86, CXCL8, FCGR3B, GZMB, ITGB2, LY86, MMP9, PPBP, and TYROBP were also differentially expressed in both the training and validation sets. Among the most promising candidates, differential expressions of ETS1, JUN, NFKB1, RELA, SP1, STAT1, ANCR, and LOC101927497 were identified via qRT-PCR experiments.
Conclusion: In this study, we identified functional modules with ncRNAs and transcription factors involved in CAVD pathogenesis. The current results suggest candidate molecules for further research on CAVD.
Keywords: bioinformatics; calcific aortic valve disease; epigenetics; non-coding RNA; transcription factor.
Copyright © 2022 Guo, Zhang, Zhang, Liu, Meng, Li, Wang, Gong and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures







References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

