Metabolic Syndrome Is Associated With Impaired Insulin-Stimulated Myocardial Glucose Metabolic Rate in Individuals With Type 2 Diabetes: A Cardiac Dynamic 18F-FDG-PET Study
- PMID: 35845046
- PMCID: PMC9276995
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.924787
Metabolic Syndrome Is Associated With Impaired Insulin-Stimulated Myocardial Glucose Metabolic Rate in Individuals With Type 2 Diabetes: A Cardiac Dynamic 18F-FDG-PET Study
Abstract
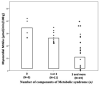
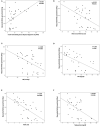
Metabolic syndrome is a condition characterized by a clustering of metabolic abnormalities associated with an increased risk of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease. An impaired insulin-stimulated myocardial glucose metabolism has been shown to be a risk factor for the development of cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. Whether cardiac insulin resistance occurs in subjects with metabolic syndrome remains uncertain. To investigate this issue, we evaluated myocardial glucose metabolic rate using cardiac dynamic 18F-FDG-PET combined with euglycemic-hyperinsulinemic clamp in three groups: a group of normal glucose tolerant individuals without metabolic syndrome (n = 10), a group of individuals with type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome (n = 19), and a group of subjects with type 2 diabetes without metabolic syndrome (n = 6). After adjusting for age and gender, individuals with type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome exhibited a significant reduction in insulin-stimulated myocardial glucose metabolic rate (10.5 ± 9.04 μmol/min/100 g) as compared with both control subjects (32.9 ± 9.7 μmol/min/100 g; P < 0.0001) and subjects with type 2 diabetes without metabolic syndrome (25.15 ± 4.92 μmol/min/100 g; P = 0.01). Conversely, as compared with control subjects (13.01 ± 8.53 mg/min x Kg FFM), both diabetic individuals with metabolic syndrome (3.06 ± 1.7 mg/min × Kg FFM, P = 0.008) and those without metabolic syndrome (2.91 ± 1.54 mg/min × Kg FFM, P = 0.01) exhibited a significant reduction in whole-body insulin-stimulated glucose disposal, while no difference was observed between the 2 groups of subjects with type 2 diabetes with or without metabolic syndrome. Univariate correlations showed that myocardial glucose metabolism was positively correlated with insulin-stimulated glucose disposal (r = 0.488, P = 0.003), and negatively correlated with the presence of metabolic syndrome (r = -0.743, P < 0.0001) and with its individual components. In conclusion, our data suggest that an impaired myocardial glucose metabolism may represent an early cardio-metabolic defect in individuals with the coexistence of type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome, regardless of whole-body insulin resistance.
Keywords: cardiac 18F-FDG-PET; cardiovascular disease; insulin resistance; metabolic syndrome; myocardial glucose metabolism; type 2 diabetes.
Copyright © 2022 Succurro, Vizza, Papa, Cicone, Monea, Tradigo, Fiorentino, Perticone, Guzzi, Sciacqua, Andreozzi, Veltri, Cascini and Sesti.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

