Inhibition of Vascular Inflammation by Apolipoprotein A-IV
- PMID: 35845068
- PMCID: PMC9279673
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.901408
Inhibition of Vascular Inflammation by Apolipoprotein A-IV
Abstract
Background: Apolipoprotein (apo) A-IV, the third most abundant apolipoprotein in human high density lipoproteins (HDLs), inhibits intestinal and systemic inflammation. This study asks if apoA-IV also inhibits acute vascular inflammation.
Methods: Inflammation was induced in New Zealand White rabbits by placing a non-occlusive silastic collar around the common carotid artery. A single 1 mg/kg intravenous infusion of lipid-free apoA-IV or saline (control) was administered to the animals 24 h before collar insertion. The animals were euthanised 24 h post-collar insertion. Human coronary artery cells (HCAECs) were pre-incubated with reconstituted HDLs containing apoA-IV complexed with phosphatidylcholine, (A-IV)rHDLs, then activated by incubation with tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-α. Cell surface vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) in the TNF-α-activated HCAECs was quantified by flow cytometry. VCAM-1, ICAM-1 and 3β-hydroxysteroid-Δ24 reductase (DHCR24) mRNA levels were quantified by real time PCR.
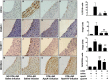
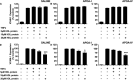
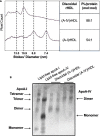
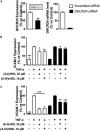
Results: Apolipoprotein ApoA-IV treatment significantly decreased collar-induced endothelial expression of VCAM-1, ICAM-1 and neutrophil infiltration into the arterial intima by 67.6 ± 9.9% (p < 0.01), 75.4 ± 6.9% (p < 0.01) and 74.4 ± 8.5% (p < 0.05), respectively. It also increased endothelial expression of DHCR24 by 2.6-fold (p < 0.05). Pre-incubation of HCAECs with (A-IV)rHDLs prior to stimulation with TNF-α inhibited VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 protein levels by 62.2 ± 12.1% and 33.7 ± 5.7%, respectively. VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 mRNA levels were decreased by 55.8 ± 7.2% and 49.6 ± 7.9%, respectively, while DHCR24 mRNA expression increased by threefold. Transfection of HCAECs with DHCR24 siRNA attenuated the anti-inflammatory effects of (A-IV)rHDLs. Pre-incubation of TNF-α-activated HCAECs with (A-IV)rHDLs also inhibited nuclear translocation of the p65 subunit of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB), and decreased IκBα phosphorylation.
Conclusion: These results indicate that apoA-IV inhibits vascular inflammation in vitro and in vivo by inhibiting NF-κB activation in a DHCR24-dependent manner.
Keywords: 3β-hydroxysteroid-Δ24 reductase; apolipoprotein A-IV; endothelial cells; high-density lipoproteins; inflammation; nuclear factor-kappaB.
Copyright © 2022 Shearston, Tan, Cochran and Rye.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Nicholls SJ, Dusting GJ, Cutri B, Bao S, Drummond GR, Rye KA, et al. Reconstituted high-density lipoproteins inhibit the acute pro-oxidant and proinflammatory vascular changes induced by a periarterial collar in normocholesterolemic rabbits. Circulation. (2005) 111:1543–50. 10.1161/01.CIR.0000159351.95399.50 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

