Autophagy in health and disease: From molecular mechanisms to therapeutic target
- PMID: 35845350
- PMCID: PMC9271889
- DOI: 10.1002/mco2.150
Autophagy in health and disease: From molecular mechanisms to therapeutic target
Abstract
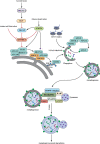
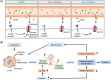
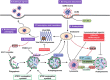
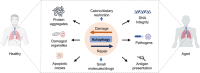
Macroautophagy/autophagy is an evolutionally conserved catabolic process in which cytosolic contents, such as aggregated proteins, dysfunctional organelle, or invading pathogens, are sequestered by the double-membrane structure termed autophagosome and delivered to lysosome for degradation. Over the past two decades, autophagy has been extensively studied, from the molecular mechanisms, biological functions, implications in various human diseases, to development of autophagy-related therapeutics. This review will focus on the latest development of autophagy research, covering molecular mechanisms in control of autophagosome biogenesis and autophagosome-lysosome fusion, and the upstream regulatory pathways including the AMPK and MTORC1 pathways. We will also provide a systematic discussion on the implication of autophagy in various human diseases, including cancer, neurodegenerative disorders (Alzheimer disease, Parkinson disease, Huntington's disease, and Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis), metabolic diseases (obesity and diabetes), viral infection especially SARS-Cov-2 and COVID-19, cardiovascular diseases (cardiac ischemia/reperfusion and cardiomyopathy), and aging. Finally, we will also summarize the development of pharmacological agents that have therapeutic potential for clinical applications via targeting the autophagy pathway. It is believed that decades of hard work on autophagy research is eventually to bring real and tangible benefits for improvement of human health and control of human diseases.
Keywords: SARS‐CoV‐2; autophagy; cancer; cardiovascular diseases; metabolic diseases; neurodegenerative diseases.
© 2022 The Authors. MedComm published by Sichuan International Medical Exchange & Promotion Association (SCIMEA) and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Canhua Huang is an editorial board member of MedComm. The paper was handled by another Editor and has undergone a rigorous peer‐review process. Author Canhua Huang was not involved in the journal's review of/or decisions related to this manuscript. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures




References
-
- de Duve C. The lysosome turns fifty. Nat Cell Biol. 2005;7(9):847‐849. - PubMed
-
- Tsukada M, Ohsumi Y. Isolation and characterization of autophagy‐defective mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEBS Lett. 1993;333(1‐2):169‐174. - PubMed
-
- Nakatogawa H, Suzuki K, Kamada Y, Ohsumi Y. Dynamics and diversity in autophagy mechanisms: lessons from yeast. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2009;10(7):458‐467. - PubMed
-
- Maruyama T, Alam JM, Fukuda T, et al. Membrane perturbation by lipidated Atg8 underlies autophagosome biogenesis. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2021;28(7):583‐593. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
