The SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro): Structure, function, and emerging therapies for COVID-19
- PMID: 35845352
- PMCID: PMC9283855
- DOI: 10.1002/mco2.151
The SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro): Structure, function, and emerging therapies for COVID-19
Abstract
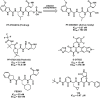
The main proteases (Mpro), also termed 3-chymotrypsin-like proteases (3CLpro), are a class of highly conserved cysteine hydrolases in β-coronaviruses. Increasing evidence has demonstrated that 3CLpros play an indispensable role in viral replication and have been recognized as key targets for preventing and treating coronavirus-caused infectious diseases, including COVID-19. This review is focused on the structural features and biological function of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) main protease Mpro (also known as 3CLpro), as well as recent advances in discovering and developing SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro inhibitors. To better understand the characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro inhibitors, the inhibition activities, inhibitory mechanisms, and key structural features of various 3CLpro inhibitors (including marketed drugs, peptidomimetic, and non-peptidomimetic synthetic compounds, as well as natural compounds and their derivatives) are summarized comprehensively. Meanwhile, the challenges in this field are highlighted, while future directions for designing and developing efficacious 3CLpro inhibitors as novel anti-coronavirus therapies are also proposed. Collectively, all information and knowledge presented here are very helpful for understanding the structural features and inhibitory mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro inhibitors, which offers new insights or inspiration to medicinal chemists for designing and developing more efficacious 3CLpro inhibitors as novel anti-coronavirus agents.
Keywords: 3‐chymotrypsin‐like protease (3CLpro); SARS‐CoV‐2; broad‐spectrum anti‐coronavirus agents; β‐coronavirus 3CLpro inhibitor.
© 2022 The Authors. MedComm published by Sichuan International Medical Exchange & Promotion Association (SCIMEA) and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
