Influence of Culture Conditions on Ex Vivo Expansion of T Lymphocytes and Their Function for Therapy: Current Insights and Open Questions
- PMID: 35845425
- PMCID: PMC9277485
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.886637
Influence of Culture Conditions on Ex Vivo Expansion of T Lymphocytes and Their Function for Therapy: Current Insights and Open Questions
Abstract
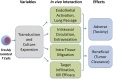
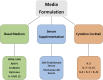
Ex vivo expansion of T lymphocytes is a central process in the generation of cellular therapies targeted at tumors and other disease-relevant structures, which currently cannot be reached by established pharmaceuticals. The influence of culture conditions on T cell functions is, however, incompletely understood. In clinical applications of ex vivo expanded T cells, so far, a relatively classical standard cell culture methodology has been established. The expanded cells have been characterized in both preclinical models and clinical studies mainly using a therapeutic endpoint, for example antitumor response and cytotoxic function against cellular targets, whereas the influence of manipulations of T cells ex vivo including transduction and culture expansion has been studied to a much lesser detail, or in many contexts remains unknown. This includes the circulation behavior of expanded T cells after intravenous application, their intracellular metabolism and signal transduction, and their cytoskeletal (re)organization or their adhesion, migration, and subsequent intra-tissue differentiation. This review aims to provide an overview of established T cell expansion methodologies and address unanswered questions relating in vivo interaction of ex vivo expanded T cells for cellular therapy.
Keywords: CAR T cell; T lymphocyte (T-cell); cell culture conditions; ex vivo expansion; homing.
Copyright © 2022 Sudarsanam, Buhmann and Henschler.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abramson J. S., Palomba M. L., Gordon L. I., Lunning M. A., Wang M., Arnason J., et al. (2020). Lisocabtagene Maraleucel for Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphomas (TRANSCEND NHL 001): a Multicentre Seamless Design Study. Lancet 396 (10254), 839–852. 10.1016/s0140-6736(20)31366-0 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Albert S., Arndt C., Feldmann A., Bergmann R., Bachmann D., Koristka S., et al. (2017). A Novel Nanobody-Based Target Module for Retargeting of T Lymphocytes to EGFR-Expressing Cancer Cells via the Modular UniCAR Platform. Oncoimmunology 6 (4), e1287246. 10.1080/2162402x.2017.1287246 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

