A Scientometric Visualization Analysis for Molecular Mechanisms of Substance Abuse and Its Neurotoxicity From 1997 to 2021
- PMID: 35845612
- PMCID: PMC9283979
- DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.885701
A Scientometric Visualization Analysis for Molecular Mechanisms of Substance Abuse and Its Neurotoxicity From 1997 to 2021
Abstract
Substance abuse has become a global problem due to drug-induced addiction and neurotoxicity, which causes a huge physical, social, and financial burden. Various kinds of drugs can hijack the users'/abusers' behavior and associated neurocircuitry. To summarize recent scientific advances on drug abuse, we reviewed relevant publications to analyze research progress and such trends through bibliometric ways. Based on retrieval strategies, a total of 681 scientific records published from 1997 to 2021 were screened and included in the Web of Science (WoS) database. Further scientometric analysis revealed that annual publication output increased across this period, with the United States of America (USA) contributing a significant number of reasons. Research has focused on neurotransmitter, oxidative stress, mitochondrial system injury, and other neurotoxic mechanisms. Neuroimmune, neurotoxic targets, and new psychoactive substances have been hot topics in recent years, which deserve continued research in the future. Specific research on molecular mechanisms has progressed across this period, with an emphasis on the root cause of toxicity and molecular targets for therapy. Moreover, collaborations of international multi-disciplinary research teams have been efficient and need to be encouraged for addiction research and the development of appropriate therapeutic processes.
Keywords: molecular mechanism; neurotoxicity; scientometric analysis; substance abuse; visualization.
Copyright © 2022 Zhang, Liu and Liang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
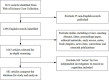
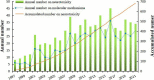
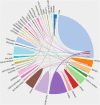
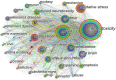
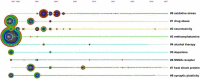
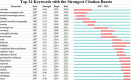
Similar articles
-
Progress and Research Trends on Catha edulis (Vahl) Endl. (Catha edulis): A Review and Bibliometric Analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Nov 11;12:705376. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.705376. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34867319 Free PMC article.
-
Global cocaine intoxication research trends during 1975-2015: a bibliometric analysis of Web of Science publications.Subst Abuse Treat Prev Policy. 2017 Feb 2;12(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s13011-017-0090-9. Subst Abuse Treat Prev Policy. 2017. PMID: 28153037 Free PMC article.
-
A bibliometric analysis of international publications and citation trends of articles in mental health produced by Chinese institutions in mainland China (1990-2019).Glob Ment Health (Camb). 2021 Sep 28;8:e37. doi: 10.1017/gmh.2021.35. eCollection 2021. Glob Ment Health (Camb). 2021. PMID: 34631113 Free PMC article.
-
A Bibliometric and Visualized Overview for the Evolution of Process Safety and Environmental Protection.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Jun 2;18(11):5985. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18115985. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34199608 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Global Trends and Hotspots in Esketamine Research: A Bibliometric Analysis of Past and Estimation of Future Trends.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022 Apr 21;16:1131-1142. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S356284. eCollection 2022. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022. PMID: 35478936 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the topic structure and abuse trends of new psychoactive Substance since the 21st century from a bibliometric perspective.Saudi Pharm J. 2024 Apr;32(4):101991. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2024.101991. Epub 2024 Feb 15. Saudi Pharm J. 2024. PMID: 38414783 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring exercise interventions in substance abuse treatment: A comprehensive bibliometric analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Dec 20;103(51):e41018. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000041018. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39705420 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association [APA] (2013). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5®). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Publishing. 10.1176/appi.books.9780890425596 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

