Hypoglycemic Effects of Lycium barbarum Polysaccharide in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Mice via Modulating Gut Microbiota
- PMID: 35845787
- PMCID: PMC9280299
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2022.916271
Hypoglycemic Effects of Lycium barbarum Polysaccharide in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Mice via Modulating Gut Microbiota
Abstract
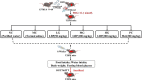
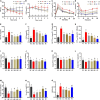
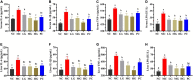
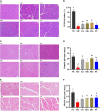
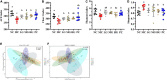
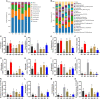
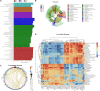
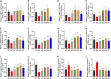
This study aims to explore the molecular mechanisms of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide (LBP) in alleviating type 2 diabetes through intestinal flora modulation. A high-fat diet (HFD) combined with streptozotocin (STZ) was applied to create a diabetic model. The results indicated that LBP effectively alleviated the symptoms of hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, and insulin resistance in diabetic mice. A high dosage of LBP exerted better hypoglycemic effects than low and medium dosages. In diabetic mice, LBP significantly boosted the activities of CAT, SOD, and GSH-Px and reduced inflammation. The analysis of 16S rDNA disclosed that LBP notably improved the composition of intestinal flora, increasing the relative abundance of Bacteroides, Ruminococcaceae_UCG-014, Intestinimonas, Mucispirillum, Ruminococcaceae_UCG-009 and decreasing the relative abundance of Allobaculum, Dubosiella, Romboutsia. LBP significantly improved the production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) in diabetic mice, which corresponded to the increase in the beneficial genus. According to Spearman's correlation analysis, Cetobacterium, Streptococcus, Ralstonia. Cetobacterium, Ruminiclostridium, and Bifidobacterium correlated positively with insulin, whereas Cetobacterium, Millionella, Clostridium_sensu_stricto_1, Streptococcus, and Ruminococcaceae_UCG_009 correlated negatively with HOMA-IR, HDL-C, ALT, AST, TC, and lipopolysaccharide (LPS). These findings suggested that the mentioned genus may be beneficial to diabetic mice's hypoglycemia and hypolipidemia. The up-regulation of peptide YY (PYY), glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), and insulin were remarkably reversed by LBP in diabetic mice. The real-time PCR (RT-PCR) analysis illustrated that LBP distinctly regulated the glucose metabolism of diabetic mice by activating the IRS/PI3K/Akt signal pathway. These results indicated that LBP effectively alleviated the hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia of diabetic mice by modulating intestinal flora.
Keywords: Lycium barbarum polysaccharide; gut microbiota; hypoglycemia; hypolipidemia; type 2 diabetes mellieus.
Copyright © 2022 Ma, Zhai, Xie, Chen, Zhang, Liu, Nie, Yuan, Tu, Tian, Zhang, Chen and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

