Effects of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms and Mediterranean Diet in Overweight or Obese Postmenopausal Women With Breast Cancer Receiving Adjuvant Hormone Therapy: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 35845810
- PMCID: PMC9284001
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2022.882717
Effects of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms and Mediterranean Diet in Overweight or Obese Postmenopausal Women With Breast Cancer Receiving Adjuvant Hormone Therapy: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
Background and aims: Weight management is recommended in overweight or obese breast cancer patients, as they have an increased risk of cancer recurrence and poor prognosis. Furthermore, identifying the relationships between genetic factors and nutrition could help suggest possible individualized nutritional solutions in weight management. The objective of this pilot randomized controlled trial was to investigate the influence of two obesity-associated single nucleotide polymorphisms and the Mediterranean diet intervention on weight loss and modification of nutrient intake and metabolic parameters in overweight or obese, postmenopausal, breast cancer patients receiving adjuvant hormone therapy.
Methods: Seventy-eight breast cancer patients were randomly assigned to the Mediterranean diet (MeDiet) group or control group, and seventy-one were finally analyzed. Body composition, nutrient intake, and metabolic parameters were assessed at baseline and after the 8-week intervention. Fat mass and obesity-associated (FTO) rs7185735 and melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4R) rs476828 variants were genotyped.
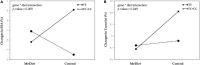
Results: We found that both variants did not influence weight loss or improvement of metabolic parameters within the Mediterranean diet intervention. Intake of saturated fatty acid (SFA) and trans fat was significantly increased in C carriers compared with the TT genotype of MC4R rs476828 only in the control group (p = 0.002 for SFA; p = 0.016 for trans fat), whereas no significant difference was observed between genotypes in the MeDiet group. There were statistically significant interactions between MC4R rs476828 and dietary intervention for changes in SFA intake (p = 0.009) and trans fat intake (p = 0.049).
Conclusion: Our data suggest that considering the effects of genotype may be more necessary when the Mediterranean diet is not followed and that this diet may have a protective role against the effects of certain genotypes. Further studies are required to determine the potential mechanism of the observed gene-diet interaction.
Clinical trial registration: [www.ClinicalTrials.gov], identifier [NCT04045392].
Keywords: FTO gene; MC4R gene; Mediterranean diet; breast cancer; nutrigenetics.
Copyright © 2022 Cho, Hong, Kwon, Choi, Lee, Kim, Bae, Ahn, Jeong and Lee.
Conflict of interest statement
K-WH and J-EC were employed by Theragen Etex Bio Institute Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Neuhouser ML, Aragaki AK, Prentice RL, Manson JE, Chlebowski R, Carty CL, et al. Overweight, obesity, and postmenopausal invasive breast cancer risk: a secondary analysis of the women’s health initiative randomized clinical trials. JAMA Oncol. (2015) 1:611–21. 10.1001/jamaoncol.2015.1546 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Robinson PJ, Bell RJ, Davis SR. Obesity is associated with a poorer prognosis in women with hormone receptor positive breast cancer. Maturitas. (2014) 79:279–86. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical