A Shorter-Bout of HIIT Is More Effective to Promote Serum BDNF and VEGF-A Levels and Improve Cognitive Function in Healthy Young Men
- PMID: 35846013
- PMCID: PMC9277476
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2022.898603
A Shorter-Bout of HIIT Is More Effective to Promote Serum BDNF and VEGF-A Levels and Improve Cognitive Function in Healthy Young Men
Abstract
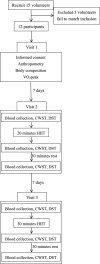
Objective: The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of single bouts of high-intensity interval training (HIIT) with different duration on serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGF-A) levels and cognitive function in healthy young men. Methods: Twelve healthy young men were participated in two HIIT treatments (20 min HIIT and 30 min HIIT) in a random order. BDNF, VEGF-A, cortisol, testosterone, blood lactic acid were measured and cognitive function was assessed by Stroop test (CWST) and Digital Span test (DST) before, immediately after, and 30 min after HIIT. Results: 20 and 30 min HIIT increased BLa (both p < 0.01), cortisol (20 min HIIT: p < 0.05; 30 min HIIT: p < 0.01), and testosterone (both p < 0.05) levels immediately when compared with their baselines. While BLa and cortisol were significantly higher in 30 min HIIT group than in 20 min HIIT group. Moreover, BDNF concentration (p < 0.01), DST-F (p < 0.01) and DST-B (p < 0.05) were increased and response time of Stroop was decreased immediately after HIIT only in 20 min HIIT group. VEGF-A concentration was increased immediately after HIIT in both groups (p < 0.01), but after 30 min recovery, it was returned to the baseline in the 20 min HIIT group and was lower than the baseline in 30 min HIIT group (p < 0.05). Conclusion: Twenty minutes HIIT is more effective than 30 minutes HIIT for promoting serum levels of BDNF and VEGF-A as well as cognitive function in healthy young men.
Keywords: BDNF; VEGF-A; cognitive function; high-intensity interval training; young men.
Copyright © 2022 Li, Zhang, Zhang, Wang, Zuo and Bo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

