Phase Ib study of avadomide (CC-122) in combination with rituximab in patients with relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and follicular lymphoma
- PMID: 35846031
- PMCID: PMC9175947
- DOI: 10.1002/jha2.394
Phase Ib study of avadomide (CC-122) in combination with rituximab in patients with relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and follicular lymphoma
Abstract
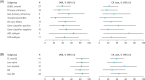
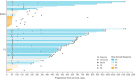
The multicenter, phase Ib CC-122-DLBCL-001 dose-expansion study (NCT02031419) explored the cereblon E3 ligase modulator (CELMoD) agent avadomide (CC-122) plus rituximab in patients with relapsed/refractory (R/R) diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) or follicular lymphoma (FL). Patients received avadomide 3 mg/day 5 days on/2 days off plus rituximab 375 mg/m2 on day 8 of cycle 1, day 1 of cycles 2 through 6, and day 1 of every third subsequent cycle for 2 years. Primary endpoints were safety and tolerability; preliminary efficacy was a secondary endpoint. A total of 68 patients were enrolled (DLBCL [n = 27], FL [n = 41; 31 lenalidomide-naïve, 10 lenalidomide-treated]). Median age was 62 years (range, 33-84 years), and patients had received a median of 3 (range, 1-8) prior regimens. Among patients with DLBCL, 66.7% had primary refractory disease (partial response or less to initial therapy). Among patients with FL, 65.9% were rituximab-refractory at study entry and 10.0% were lenalidomide-refractory. The most common any-grade avadomide-related adverse events (AEs) were neutropenia (63.2%), infections/infestations (23.5%), fatigue (22.1%), and diarrhea (19.1%). The most common grade 3/4 avadomide-related AEs were neutropenia (55.9%) infections/infestations (8.8%), and febrile neutropenia (7.4%). In patients with DLBCL, overall response rate (ORR) was 40.7% and median duration of response (mDOR) was 8.0 months. In patients with FL, ORR was 80.5% and mDOR was 27.6 months; response rates were similar in lenalidomide-naïve and -treated patients. Avadomide plus rituximab was well tolerated, and preliminary antitumor activity was observed in patients with R/R DLBCL and FL, including subgroups with typically poor outcomes. These results support further investigation of novel CELMoD agents in combination with rituximab in R/R DLBCL and FL.
Keywords: CELMoD; avadomide; diffuse large B‐cell lymphoma; follicular lymphoma.
© 2022 The Authors. eJHaem published by British Society for Haematology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Loretta J. Nastoupil received honoraria from ADC Therapeutics, Bayer, Celgene, a Bristol Myers Squibb Company, Epizyme, Genentech, Gilead, Janssen, MorphoSys, Novartis, Pfizer, and TG Therapeutics; and received research funding from Bristol Myers Squibb/Celgene, Epizyme, Genentech, Janssen, Novartis, and TG Therapeutics. John Kuruvilla received honoraria from Amgen, Antengene, AstraZeneca, Celgene, a Bristol Myers Squibb company Gilead, Incyte, Janssen, Karyopharm, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Seattle Genetics, and TG Therapeutics; served as a consultant or advisor for AbbVie, Bristol Myers Squibb, Gilead, Karyopharm, Merck, Roche, and Seattle Genetics; and received research funding from AstraZeneca, Janssen, Roche, and Merck. Julio C. Chavez served as a consultant or advisor for AstraZeneca, Bayer, Celgene, a Bristol Myers Squibb Company, Genentech, Karyopharm, Morphosys, Novartis, Verastem, and Pfizer; received research funding from Merck; and served on the speaker's bureau for Genentech and AstraZeneca. Fontanet Bijou served as consultant or advisor for Bristol Myers Squibb and AbbVie. Armando Santoro served as consultant or advisor for Arqule, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eisai, Gilead, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Pfizer, Sanofi, and Servier, and served on speaker's bureau for AbbVie, Amgen, Arqule, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, a Bristol Myers Squibb Company, Eisai, Gilead, Lilly, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Sandoz, Servier, and Takeda. Ian W. Flinn served as consultant or advisor for AbbVie, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Genentech, Gilead Sciences, Great Point Partners, Iksuda Therapeutics, Janssen, Juno Therapeutics, Kite Pharma, MorphoSys, Novartis, Nurix Therapeutics, Pharmacyclics, Roche, Seattle Genetics, Takeda, TG Therapeutics, Unum Therapeutics, Verastem, and Yingli Pharmaceuticals; and received research funding from AbbVie, Acerta Pharma, Agios, ArQule, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Calithera Biosciences, Celgene, a Bristol Myers Squibb Company, Constellation Pharmaceuticals, Curis, Forma Therapeutics, Forty‐Seven, Genentech, Gilead Sciences, IGM Biosciences, Incyte, Infinity Pharmaceuticals, Janssen, Juno Therapeutics, Karyopharm Therapeutics, Kite Pharma, Loxo, Merck, MorphoSys, Novartis, Pfizer, Pharmacyclics, Portola Pharmaceuticals, Rhizen Pharmaceuticals, Roche, Seattle Genetics, Takeda, Teva, TG Therapeutics, Trillium Therapeutics, Triphase Research & Development Corp., Unum Therapeutics, and Verastem. Vaishalee P. Kenkre received research funding from AbbVie, Celgene, a Bristol Myers Squibb Company, MEI Pharma, and Novartis. P. Corradini received honoraria from AbbVie, ADC Therapeutics, Amgen, Celgene, a Bristol Myers Squibb Company, Daiichi Sankyo, Gilead, Incyte, Janssen, Kite, KyowaKirin, Novartis, Roche, Sanofi, and Takeda; served as consultant or advisor for AbbVie, ADC Therapeutics, Amgen, Celgene, a Bristol Myers Squibb Company, Daiichi Sankyo, Gilead, Incyte, Janssen, Kite, KyowaKirin, Novartis, Roche, Sanofi, and Takeda; and received travel funding from Novartis, Janssen, Celgene, a Bristol Myers Squibb Company, Bristol Myers Squibb, Takeda, Gilead, Amgen, and AbbVie. Iris Isufi served as a consultant or advisor for AstraZeneca, Bayer, Celgene, a Bristol Myers Squibb Company, Epizyme, and Kite. David J. Andorsky served as consultant or advisor for AbbVie and Bristol Myers Squibb and received research funding from AstraZeneca, Celgene, a Bristol Myers Squibb company, and Epizyme. Daniel Greenwald served as consultant or advisor for AstraZeneca and served on the speaker's bureau for Genentech and Jazz. R. Sangha received honoraria from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli‐Lilly, Merck, Mylan, Pfizer, Roche/Genentech, Sanofi, Takeda, and Teva, and served as consultant or advisor for AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli‐Lilly, Merck, Roche/Genentech, Sanofi, Takeda, and Teva. Patrick Hagner, Nian Gong, Shailaja Uttamsingh, and Michael Pourdehnad are employed by and have equity ownership with Bristol Myers Squibb. Frank Shen, Yan Li, and Juergen Dobmeyer are employed by Bristol Myers Squibb. Vincent Ribrag received honoraria from AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Incyte, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, and Roche; served as a consultant or advisor for AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, and Roche; received research funding from argenX, Astex, and GlaxoSmithKline; and received travel funding from AstraZeneca. No disclosures were reported by the other authors.
Figures

References
-
- Armitage JO, Gascoyne RD, Lunning MA, Cavalli F. Non‐Hodgkin lymphoma. Lancet 2017;390:298–310. - PubMed
-
- Liu Y, Barta SK. Diffuse large B‐cell lymphoma: 2019 update on diagnosis, risk stratification, and treatment. Am J Hematol. 2019;94:604–16. - PubMed
-
- Salles GA. Clinical features, prognosis and treatment of follicular lymphoma. Hematol Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2007:216–25. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
