In silico Identification of miRNAs and Their Targets in Cluster Bean for Their Role in Development and Physiological Responses
- PMID: 35846150
- PMCID: PMC9280363
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.930113
In silico Identification of miRNAs and Their Targets in Cluster Bean for Their Role in Development and Physiological Responses
Abstract
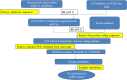
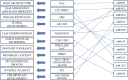
Cluster bean popularly known as "guar" is a drought-tolerant, annual legume that has recently emerged as an economically important crop, owing to its high protein and gum content. The guar gum has wide range of applications in food, pharma, and mining industries. India is the leading exporter of various cluster bean-based products all across the globe. Non-coding RNAs (miRNAs) are involved in regulating the expression of the target genes leading to variations in the associated pathways or final protein concentrations. The understanding of miRNAs and their associated targets in cluster bean is yet to be used to its full potential. In the present study, cluster bean EST (Expressed Sequence Tags) database was exploited to identify the miRNA and their predicted targets associated with metabolic and biological processes especially response to diverse biotic and abiotic stimuli using in silico approach. Computational analysis based on cluster bean ESTs led to the identification of 57 miRNAs along with their targets. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report on identification of miRNAs and their targets using ESTs in cluster bean. The miRNA related to gum metabolism was also identified. Most abundant miRNA families predicted in our study were miR156, miR172, and miR2606. The length of most of the mature miRNAs was found to be 21nt long and the range of minimal folding energy (MFE) was 5.8-177.3 (-kcal/mol) with an average value of 25.4 (-kcal/mol). The identification of cluster bean miRNAs and their targets is predicted to hasten the miRNA discovery, resulting in better knowledge of the role of miRNAs in cluster bean development, physiology, and stress responses.
Keywords: cluster bean (Cyamopsis tetragonoloba L. Taub.); galactomannan; miRNA identification; miRNA targets; micro RNAs (miRNAs); non coding RNAs.
Copyright © 2022 Chaudhary, Jangra and Yadav.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Drought Stress Response in Guar (Cyamopsis tetragonoloba (L.) Taub): Physiological and Molecular Genetic Aspects.Plants (Basel). 2023 Nov 24;12(23):3955. doi: 10.3390/plants12233955. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38068592 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In silico identification and characterization of conserved miRNAs and their target genes in sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas L.) expressed sequence tags (ESTs).Plant Signal Behav. 2013;8(12):e26543. doi: 10.4161/psb.26543. Epub 2013 Sep 25. Plant Signal Behav. 2013. PMID: 24067297 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of cDNA libraries from developing seeds of guar (Cyamopsis tetragonoloba (L.) Taub).BMC Plant Biol. 2007 Nov 23;7:62. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-7-62. BMC Plant Biol. 2007. PMID: 18034910 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide discovery of tissue-specific miRNAs in clusterbean (Cyamopsis tetragonoloba) indicates their association with galactomannan biosynthesis.Plant Biotechnol J. 2018 Jun;16(6):1241-1257. doi: 10.1111/pbi.12866. Epub 2018 Mar 11. Plant Biotechnol J. 2018. PMID: 29193664 Free PMC article.
-
Role of microRNAs in biotic and abiotic stress responses in crop plants.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2014 Sep;174(1):93-115. doi: 10.1007/s12010-014-0914-2. Epub 2014 May 29. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 24869742 Review.
Cited by
-
Drought Stress Response in Guar (Cyamopsis tetragonoloba (L.) Taub): Physiological and Molecular Genetic Aspects.Plants (Basel). 2023 Nov 24;12(23):3955. doi: 10.3390/plants12233955. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38068592 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hairpin in a haystack: In silico identification and characterization of plant-conserved microRNA in Rafflesiaceae.Open Life Sci. 2025 Jan 27;20(1):20221033. doi: 10.1515/biol-2022-1033. eCollection 2025. Open Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 39881826 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al-Qurainy F., Alshameri A., Gaafar A. R., Khan S., Nadeem M., Alameri A. A., et al. (2019). Comprehensive Stress-Based De Novo Transcriptome Assembly and Annotation of Guar (Cyamopsis tetragonoloba (L.) Taub.): An Important Industrial and Forage Crop. Int. J. Genomics. 2019, 7295859. 10.3390/plants1103029110.1155/2019/7295859 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bhatt R. K., Sharma R., Mahla H. R., Kalia R. K. (2016). Guar Production, Utilization and Marketing: Current Scenario and Future Prospects. Jodhpur: Central Arid Zone Research Institute, 1–40.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

