Association of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Liver Stiffness With Bone Mineral Density in American Adults
- PMID: 35846319
- PMCID: PMC9280639
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.891382
Association of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Liver Stiffness With Bone Mineral Density in American Adults
Abstract
Contest: The relationship between metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) and liver stiffness and bone mineral density (BMD) remains unclear.
Objectives: We aimed to investigate the association between MAFLD and liver stiffness and BMD in the United States population.
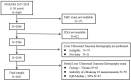
Methods: A cross-sectional study among 2031 participants over 50 years old in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2017-2018 was performed. All patients underwent vibration controlled transient elastography (VCTE) and dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA). The linear and logistic regression model were used to analyze the association between the MAFLD and liver stiffness and osteoporosis, with adjustments for known covariates. Furthermore, the sensitive analyses were conducted to explore the relationship between MAFLD and liver stiffness and whole osteoporosis (include femoral and lumbar osteoporosis).
Results: MAFLD was prevalent in the study population, with a prevalence of 50.9% for men and 40.7% for women. The multiple linear models demonstrated positive associations between MAFLD and liver stiffness and total femur BMD, femur neck BMD, trochanter BMD, intertrochanter BMD. In multiple logistic regression models, both MAFLD and significant liver fibrosis were negatively associated with femoral osteoporosis (OR=0.41, 95% CI: 0.27 to 0.63; OR=0.67, 95% CI: 0.33-1.37, respectively). Nonetheless, when BMI was adjusted, the association between MAFLD and liver stiffness and osteoporosis became insignificant. Besides, as showed in the sensitive analyses, the relationship between MAFLD and liver stiffness and whole osteoporosis were stable.
Conclusions: These results suggest that MAFLD and liver stiffness were associated with higher femoral and lumbar bone mineral density in individuals aged over 50 years. But the results may be confounded by BMI.
Keywords: Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease; National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey; Osteoporosis; bone mineral density; cross-sectional study.
Copyright © 2022 Li, Luo, Zhang, Liu and Lin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Associations of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease and hepatic fibrosis with bone mineral density and risk of osteopenia/osteoporosis in T2DM patients.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Dec 4;14:1278505. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1278505. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 38116314 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic associated fatty liver disease and bone mineral density: a cross-sectional study of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2017-2018.Osteoporos Int. 2023 Apr;34(4):713-724. doi: 10.1007/s00198-023-06687-w. Epub 2023 Jan 31. Osteoporos Int. 2023. PMID: 36719471
-
NAFLD and Liver Fibrosis Are Not Associated With Reduced Femoral Bone Mineral Density in the General US Population.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021 Jul 13;106(8):e2856-e2865. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgab262. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021. PMID: 33878156
-
Association between fatty liver index and controlled attenuation parameters as markers of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease and bone mineral density: observational and two-sample Mendelian randomization studies.Osteoporos Int. 2024 Apr;35(4):679-689. doi: 10.1007/s00198-023-06996-0. Epub 2024 Jan 15. Osteoporos Int. 2024. PMID: 38221591
-
MAFLD: what 2 years of the redefinition of fatty liver disease has taught us.Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab. 2022 Nov 22;13:20420188221139101. doi: 10.1177/20420188221139101. eCollection 2022. Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab. 2022. PMID: 36439029 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The effects of raspberry consumption on anthropometric indices and liver function tests in adults: a GRADE-assessed systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Nutr. 2024 Aug 5;11:1419417. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1419417. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39161910 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease and hepatic fibrosis with bone mineral density and risk of osteopenia/osteoporosis in T2DM patients.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Dec 4;14:1278505. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1278505. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 38116314 Free PMC article.
-
The Inter-Organ Crosstalk Reveals an Inevitable Link between MAFLD and Extrahepatic Diseases.Nutrients. 2023 Feb 23;15(5):1123. doi: 10.3390/nu15051123. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 36904122 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and bone mineral density: Mendelian randomization and mediation analysis.Bone Rep. 2024 Jun 26;22:101785. doi: 10.1016/j.bonr.2024.101785. eCollection 2024 Sep. Bone Rep. 2024. PMID: 39220175 Free PMC article.
-
Optimal body mass index for protecting middle-aged and elderly patients with fatty liver from future fractures.Endocr Connect. 2024 Jul 3;13(8):e240089. doi: 10.1530/EC-24-0089. Print 2024 Aug 1. Endocr Connect. 2024. PMID: 38819306 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical