Mutagenicity assessment of Salacia chinensis by bacterial reverse mutation assay using histidine dependent Salmonella typhimurium tester strains
- PMID: 35846385
- PMCID: PMC9283664
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2022.103370
Mutagenicity assessment of Salacia chinensis by bacterial reverse mutation assay using histidine dependent Salmonella typhimurium tester strains
Abstract
Background and objective: Genotoxicity analysis is one of the most important non-clinical environmental safety investigations required for pharmaceutical and agrochemical product registration. Any medicinal product must undergo a risk evaluation to determine its mutagenicity and carcinogenicity.
Materials and methods: The Ames test is a commonly used in vitro test for determining a test chemical's mutagenic activity. Histidine-dependent Salmonella typhimurium strains with a defective gene that causes the bacteria to synthesis the necessary amino acid histidine for life were tested for mutagenic potential. In order to reveal pro-mutagens and mutagens, the mutagenic potential of both plate integration and pre-incubation techniques was examined in the presence and absence of metabolizing system. Salacia chinensis has been widely used in ayurveda to treat various ailments. However, the information of mutagenicity of Salacia chinensis is scarce as per available literature.
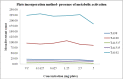
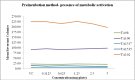
Results: The mutagenicity of a Salacia chinensis root extract was investigated utilizing the Ames assay with plate incorporation and pre-incubation protocols using the appropriate Salmonella typhimurium tester strains: TA98, TA100, TA1537, TA1535, and TA102 in the presence and absence of S9. The concentrations used were 0.3123, 0.625, 1.25, 2.5 and 5 mg/plate. The extract of Salacia chinensis root did not show any mutagenic effect in any of the Salmonella typhimurium strains at the concentrations tested in the absence or presence of metabolic activation.
Conclusion: The root of Salacia chinensis was hence confirmed to be non-mutagenic and at least according to the results of this genotoxicity evaluation can be regarded as being safe for human use.
Keywords: Ames test; Mangiferin; Mutagenecity; Salacia chinensis; Salmonella typhimurium.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Synacinn™: Bacterial reverse mutation test data in five histidine-requiring strains of Salmonella Typhimurium.Data Brief. 2021 May 7;36:107075. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2021.107075. eCollection 2021 Jun. Data Brief. 2021. PMID: 34041312 Free PMC article.
-
The mutagenic assessment of an electronic-cigarette and reference cigarette smoke using the Ames assay in strains TA98 and TA100.Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2016 Dec;812:29-38. doi: 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2016.10.005. Epub 2016 Oct 29. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2016. PMID: 27908385
-
Bacterial photomutagenicity testing: distinction between direct, enzyme-mediated and light-induced events.Mutat Res. 1996 Sep 26;361(1):41-8. doi: 10.1016/s0165-1161(96)90228-9. Mutat Res. 1996. PMID: 8816942
-
Mutagenic potential of medicinal plants evaluated by the Ames Salmonella/microsome assay: A systematic review.Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2020 Oct-Dec;786:108338. doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2020.108338. Epub 2020 Oct 18. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2020. PMID: 33339578
-
Mutagenicity of carcinogenic heterocyclic amines in Salmonella typhimurium YG strains and transgenic rodents including gpt delta.Genes Environ. 2021 Sep 16;43(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s41021-021-00207-0. Genes Environ. 2021. PMID: 34526143 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A perspective review on factors that influence mutagenicity in medicinal plants and their health implications.Toxicol Sci. 2025 Apr 1;204(2):121-142. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfaf004. Toxicol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39804670 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Carneirol C.C., Silva C.R., Menezes A.C.S., Pérez C.N., Chen-Chen L. Assessment of genotoxic, cytotoxic, and protective effects of Salacia crassifolia (Mart. Ex. Schult.) G. Don. stem bark fractions in mice. Genet. Mol. Res. 2013;12(3):2167–2177. - PubMed
-
- Chavan J.J., Ghadage D.M., Bhoite A.S., Umdale S.D. Micropropagation, molecular profiling and RP-HPLC determination of mangiferin across various regeneration stages of Saptarangi (Salacia chinensis L.) Ind. Crops Prod. 2015;76:1123–1132.
-
- Flammang A.M., Erexson G.L., Mecchi M.S., Murli H. Genotoxicity testing of a Salacia oblonga extract. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2006;44(11):1868–1874. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

