Perceived Stigma and Its Association with Gender and Disclosure Status among People Living with HIV/AIDS and Attending Antiretroviral Therapy Clinics in Ethiopia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 35846569
- PMCID: PMC9287106
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/3246249
Perceived Stigma and Its Association with Gender and Disclosure Status among People Living with HIV/AIDS and Attending Antiretroviral Therapy Clinics in Ethiopia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: The psychological experience of being rejected, blamed, and ashamed in relation to a recognized medical disease is known as perceived stigma. It has a close connection to psychological health and therapy afterward. To the best of our knowledge, there has not been any national systematic review and meta-analysis research on this topic. Therefore, we conducted this analysis to thoroughly evaluate the pooled prevalence of perceived stigma among HIV/AIDS patients in Ethiopia who are receiving antiretroviral therapy and its relationship to gender differences and disclosure status.
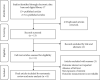
Method: We investigated the eight databases for quantitative Ethiopian studies published in English from 2008 to 2021 that looked at the relationship between felt stigma, gender, and disclosure status. To meet the statistical requirements of a systematic review and meta-analysis analysis, the random effect model for pooled prevalence of perceived stigma, log odds ratio for associated variables, I-squared statistics for heterogeneity, and Egger's test for publication bias were implemented. The Joanna Briggs Institute Meta-Analysis of Statistics Assessment and Review Instrument's standard data extraction method was performed to collect the necessary data, and STATA-14 statistical software was used for analysis.
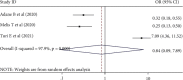
Result: A total of 8 cross-sectional Ethiopian studies with 3,857 participants were integrated into this systematic review and meta-analysis study. The pooled prevalence of perceived stigma among people living with HIV/AIDS and attending antiretroviral therapy in Ethiopia was OR = 50.36% (95% CI: (40.71, 60.00), I 2 = 97.3%, p=0.000 ). The pooled odds ratio of being male was 0.95 (95% CI: 0.53, 1.68, I 2 = 86.7%, p=0.000) and disclosure status was 0.84 (95% CI: 0.09, 7.89, I 2 = 97.9%, p=0.000).
Conclusion: In this study, half of the participants encountered stigma. There was no statistically significant correlation between gender difference, disclosure status, and the perception of stigma. To address the mental and psychological issues of people living with HIV/AIDS, it is necessary to look into other factors that influence perceived stigma. It is recommended to screen for and treat perceived stigma with prompt examination and follow-up.
Copyright © 2022 Chalachew Kassaw et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Ainlay S. C., Coleman L. M., Becker G. The Dilemma of Difference . Berlin, Germany: Springer; 1986. Stigma reconsidered; pp. 1–13.
-
- HIV/AIDS JUNPo. Report on the Global HIV/AIDS Epidemic . Geneva, Switzerland: UNAIDS; 2002.
-
- Mehta K. G., Baxi R., Patel S., Chavda P., Mazumdar V. Stigma, discrimination, and domestic violence experienced by women living with HIV: a cross-sectional study from western India. Indian Journal of Community Medicine: Official Publication of Indian Association of Preventive & Social Medicine . 2019;44(4):p. 373. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

