Learning Deficits Induced by High-Calorie Feeding in the Rat are Associated With Impaired Brain Kynurenine Pathway Metabolism
- PMID: 35846874
- PMCID: PMC9277427
- DOI: 10.1177/11786469221111116
Learning Deficits Induced by High-Calorie Feeding in the Rat are Associated With Impaired Brain Kynurenine Pathway Metabolism
Abstract
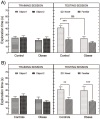
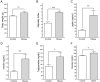
In addition to be a primary risk factor for type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease, obesity is associated with learning disabilities. Here we examined whether a dysregulation of the kynurenine pathway (KP) of tryptophan (Trp) metabolism might underlie the learning deficits exhibited by obese individuals. The KP is initiated by the enzymatic conversion of Trp into kynurenine (KYN) by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO). KYN is further converted to several signaling molecules including quinolinic acid (QA) which has a negative impact on learning. Wistar rats were fed either standard chow or made obese by exposure to a free choice high-fat high-sugar (fcHFHS) diet. Their learning capacities were evaluated using a combination of the novel object recognition and the novel object location tasks, and the concentrations of Trp and KYN-derived metabolites in several brain regions determined by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Male, but not female, obese rats exhibited reduced learning capacity characterized by impaired encoding along with increased hippocampal concentrations of QA, Xanthurenic acid (XA), Nicotinamide (Nam), and oxidized Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+). In contrast, no differences were detected in the serum levels of Trp or KP metabolites. Moreover, obesity enhanced the expression in the hippocampus and frontal cortex of kynurenine monooxygenase (KMO), an enzyme involved in the production of QA from kynurenine. QA stimulates the glutamatergic system and its increased production leads to cognitive impairment. These results suggest that the deleterious effects of obesity on cognition are sex dependent and that altered KP metabolism might contribute to obesity-associated learning disabilities.
Keywords: Tryptophan; brain; kynurenine; learning; memory; obesity.
© The Author(s) 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures





References
-
- Blüher M. Obesity: global epidemiology and pathogenesis. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2019;15:288-298. - PubMed
-
- Dye L, Boyle NB, Champ C, Lawton C. The relationship between obesity and cognitive health and decline. Proc Nutr Soc. 2017;76:443-454. - PubMed
-
- Cournot M, Marquié JC, Ansiau D, et al. Relation between body mass index and cognitive function in healthy middle-aged men and women. Neurology. 2006;67:1208-1214. - PubMed
-
- Pignatti R, Bertella L, Albani G, Mauro A, Molinari E, Semenza C. Decision-making in obesity: a study using the gambling task. Eat Weight Disord. 2006;11:126-132. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

