Variability of Reaction Time as a Marker of Executive Function Impairments in Fibromyalgia
- PMID: 35846978
- PMCID: PMC9277204
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/1821684
Variability of Reaction Time as a Marker of Executive Function Impairments in Fibromyalgia
Abstract
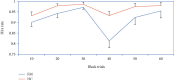
In addition to chronic widespread pain and depression and anxiety symptoms, patients with fibromyalgia frequently experience cognitive problems. This study investigated executive functions in fibromyalgia via a Go/No-Go task. To obtain comprehensive information about performance, traditional and ex-Gaussian parameters of reaction time (RT) variability were used, in addition to speed and accuracy indices. Ex-Gaussian parameters show an excellent fit to empirical RT distributions. Fifty-two female fibromyalgia patients and twenty-eight healthy controls participated. The task included 60 visual stimuli, which participants had to respond to (Go stimuli) or withhold the response to (No-Go stimuli). After 30 trials, the task rule changed, such that previous No-Go stimuli had to be responded to. Performance was indexed by the hit rate, false alarm rate, and mean (M) and intraindividual standard deviation (SD) of RT and the ex-Gaussian parameters mu, sigma, and tau. Mu and sigma indicate the M and SD of the Gaussian distribution; tau reflects the M and SD of the exponential function. Patients exhibited a lower hit rate, higher M RT, and higher tau than controls. Moreover, patients showed greater decrease of the hit rate after the change of task rule. In the entire sample, SD, sigma, and tau were inversely associated with the hit rate and positively associated with the false alarm rate. While the greater decline in hit rate after the change in task rule indicates deficient cognitive flexibility, the lack of any difference in false alarm rate suggests intact response inhibition. Higher M RT reflects reduced cognitive or motor speed. Increased tau in fibromyalgia indicates greater fluctuations in executive control and more frequent temporary lapses of attention. For the first time, this study demonstrated that indices of RT variability, in particular those derived from the ex-Gaussian function, may complement speed and accuracy parameters in the assessment of executive function impairments in fibromyalgia. Optimized assessment may facilitate the personalization of therapies aimed at improving the cognitive function of those with the disorder.
Copyright © 2022 Stefan Duschek et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials