Hepatoprotective Efficacy and Interventional Mechanism of Qijia Rougan Decoction in Liver Fibrosis
- PMID: 35846987
- PMCID: PMC9283647
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.911250
Hepatoprotective Efficacy and Interventional Mechanism of Qijia Rougan Decoction in Liver Fibrosis
Abstract
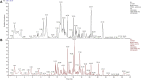
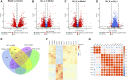
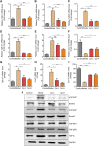
Liver fibrosis is a leading contributor to chronic liver diseases such as cirrhosis and liver cancer, which pose a serious health threat worldwide, and there are no effective drugs to treat it. Qijia Rougan decoction was modified from Sanjiasan, a traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) described in the "Wenyilun" manuscript. Qijia Rougan decoction possesses hepatoprotective and antifibrotic effects for clinical applications. However, its underlying mechanisms remain largely unknown. In this study, fibrotic rats induced by carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) were treated with two doses of Qijia Rougan decoction. Histopathological and serum biochemical analyses were carried out to assess liver structure and function, respectively. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) coupled with mass spectrometry (MS) was performed to identify bioactive compositions in Qijia Rougan decoction. Transcriptome analysis using mRNA-sequencing (mRNA-Seq) was used to explore the underlying mechanisms and verified by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and Western blotting. Qijia Rougan decoction significantly attenuated CCl4-induced hepatic fibrotic injury, supported by promoted liver function and improved liver fibrosis. Eight main representative components originating from raw materials in the Qijia Rougan decoction were found to possess an antifibrotic role. Mechanistically, Qijia Rougan decoction regulated biological processes such as oxidation-reduction, fatty acid metabolism, cell adhesion, and transforming growth factor beta (TGFβ) signaling. We determined that Qijia Rougan decoction reversed the expression of inflammatory cytokines and inhibited the activation of fibrosis-related TGFβ signaling. It also reversed the deterioration of liver structure and function in rats induced by CCl4. Overall, Qijia Rougan decoction significantly mediated metabolism-associated processes, inhibited inflammatory reactions, and repressed fibrosis-related TGFβ signaling, which prevented liver fibrosis deterioration. Our study deepens our understanding of TCM in the diagnosis and treatment of liver fibrosis.
Keywords: inflammation; liver fibrosis; qijia rougan decoction; transcriptomics; transforming growth factor beta.
Copyright © 2022 Chen, Wang, Ji, Sun, Feng, Yu and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

