Left ventricular thrombus in the multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children associated with COVID-19
- PMID: 35847408
- PMCID: PMC9280099
- DOI: 10.4103/apc.apc_82_21
Left ventricular thrombus in the multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children associated with COVID-19
Abstract
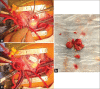
A 3-year-old girl presenting with fever, mucocutaneous inflammation, and acute gastrointestinal symptoms met criteria for the multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children associated with COVID-19 (MIS-C). Echocardiography showed severely decreased left ventricular (LV) function with an apical mass. After treatment with intravenous (IV) immunoglobulin, IV steroids, anakinra, milrinone, and systemic anticoagulation, her LV function rapidly improved and the mass became increasingly mobile. Given the risk of systemic embolization, the mass was excised through left ventriculotomy and pathology confirmed a thrombus.
Keywords: Left ventricular thrombus; multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children; severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; surgery.
Copyright: © 2022 Annals of Pediatric Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Blumfield E, Levin TL, Kurian J, Lee EY, Liszewski MC. Imaging findings in Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C) Associated With Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2021;216:507–17. - PubMed
-
- Stratton JR, Resnick AD. Increased embolic risk in patients with left ventricular thrombi. Circulation. 1987;75:1004–11. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous