Unraveling the drug distribution in brain enabled by MALDI MS imaging with laser-assisted chemical transfer
- PMID: 35847487
- PMCID: PMC9279630
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.11.007
Unraveling the drug distribution in brain enabled by MALDI MS imaging with laser-assisted chemical transfer
Abstract
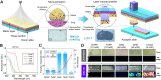
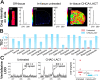
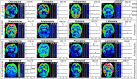
Accurate localization of central nervous system (CNS) drug distribution in the brain is quite challenging to matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) mass spectrometry imaging (MSI), owing to the ionization competition/suppression of highly abundant endogenous biomolecules and MALDI matrix. Herein, we developed a highly efficient sample preparation technique, laser-assisted chemical transfer (LACT), to enhance the detection sensitivity of CNS drugs in brain tissues. A focused diode laser source transilluminated the tissue slide coated with α-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid, an optimal matrix to highly absorb the laser radiation at 405 nm, and a very thin-layer chemical film mainly containing drug molecule was transferred to the acceptor glass slide. Subsequently, MALDI MSI was performed on the chemical film without additional sample treatment. One major advantage of LACT is to minimize ionization competition/suppression from the tissue itself by removing abundant endogenous lipid and protein components. The superior performance of LACT led to the successful visualization of regional distribution patterns of 16 CNS drugs in the mouse brain. Furthermore, the dynamic spatial changes of risperidone and its metabolite were visualized over a 24-h period. Also, the brain-to-plasma (B/P) ratio could be obtained according to MALDI MSI results, providing an alternative means to assess brain penetration in drug discovery.
Keywords: Brain penetration; Drug distribution; Laser-assisted chemical transfer; Mass spectrometry imaging; Pharmaceutical analysis.
© 2022 Chinese Pharmaceutical Association and Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.
Figures
References
-
- Mullard A. New drugs cost US $2.6 billion to develop. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2014;13:877.
-
- Morgan P., Brown D.G., Lennard S., Anderton M.J., Barrett J.C., Eriksson U., et al. Impact of a five-dimensional framework on R&D productivity at AstraZeneca. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2018;17:167. - PubMed
-
- Di L., Kerns E.H., Carter G.T. Strategies to assess blood–brain barrier penetration. Expet Opin Drug Discov. 2008;3:677–687. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

