Silica nanoparticles as novel sustainable approach for plant growth and crop protection
- PMID: 35847613
- PMCID: PMC9284391
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09908
Silica nanoparticles as novel sustainable approach for plant growth and crop protection
Abstract
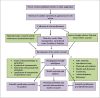
Agriculture crops encounter several biotic and abiotic stresses, including pests, diseases, nutritional deficits, and climate change, which necessitate the development of new agricultural technologies. By developing nano-based fertilizers, insecticides and herbicides, and early disease diagnostics, nanotechnology may help to increase agricultural crop quality and production. The application of silica nanoparticles (SiNPs) may be the solution for increasing the yield to combat the agriculture crisis in the near future. SiNPs have unique physiological properties, such as large surface area, aggregation, reactivity, penetrating ability, size, and structure, which enable them to penetrate plants and regulate their metabolic processes. Pesticide delivery, enhanced nutrition supply, disease management, and higher photosynthetic efficiency and germination rate are all attributed to SiNPs deposition on plant tissue surfaces. SiNPs have been demonstrated to be non-toxic in nature, making them suitable for usage in agriculture. In this regard, the current work provides the most important and contemporary applications of SiNPs in agriculture as well as biogenic and non-biogenic synthetic techniques. As a result, this review summarizes the literature on SiNPs and explores the use of SiNPs in a variety of agricultural disciplines.
Keywords: Agricultural-waste; Fertilizers; Herbicides; Pesticides; Silica nanoparticles.
© 2022 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Silicon nanoparticles in sustainable agriculture: synthesis, absorption, and plant stress alleviation.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Mar 28;15:1393458. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1393458. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38606077 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Silicon nanoparticles (SiNPs) in sustainable agriculture: major emphasis on the practicality, efficacy and concerns.Nanoscale Adv. 2021 May 31;3(14):4019-4028. doi: 10.1039/d1na00233c. eCollection 2021 Jul 13. Nanoscale Adv. 2021. PMID: 36132841 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanotechnology, a frontier in agricultural science, a novel approach in abiotic stress management and convergence with new age medicine-A review.Sci Total Environ. 2024 Feb 20;912:169097. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.169097. Epub 2023 Dec 5. Sci Total Environ. 2024. PMID: 38056665 Review.
-
Nanotechnology for sustainable agro-food systems: The need and role of nanoparticles in protecting plants and improving crop productivity.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2023 Jan;194:533-549. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2022.12.004. Epub 2022 Dec 9. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2023. PMID: 36521290 Review.
-
Nanoparticles as catalysts of agricultural revolution: enhancing crop tolerance to abiotic stress: a review.Front Plant Sci. 2025 Jan 17;15:1510482. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1510482. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 39898270 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Synergistic application of melatonin and silicon oxide nanoparticles modulates reactive oxygen species generation and the antioxidant defense system: a strategy for cadmium tolerance in rice.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Oct 15;15:1484600. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1484600. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 39474214 Free PMC article.
-
Agronomic Investigation of Spray Dispersion of Metal-Based Nanoparticles on Sunflowers in Real-World Environments.Plants (Basel). 2023 Apr 27;12(9):1789. doi: 10.3390/plants12091789. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37176847 Free PMC article.
-
Complexation and immobilization of arsenic in maize using green synthesized silicon nanoparticles (SiNPs).Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 14;14(1):6176. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-56924-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38486015 Free PMC article.
-
Valorizing Banana Peel Waste into Mesoporous Biogenic Nanosilica and Novel Nano-biofertilizer Formulation Thereof via Nano-biopriming Inspired Tripartite Interaction Studies.ACS Omega. 2025 Feb 5;10(6):5537-5553. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c08152. eCollection 2025 Feb 18. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 39989758 Free PMC article.
-
Unravelling the effects of nano SiO2, nano TiO2 and their nanocomposites on Zea mays L. growth and soil health.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 18;14(1):13996. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-61456-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38886471 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adebisi J.A., Agunsoye J.O., Bello S.A., Haris M., Ramakokovhu M.M., Daramola M.O., Hassan S.B. Green production of silica nanoparticles from maize stalk. Part. Sci. Technol. 2020;38(6):667–675.
-
- Adebisi J., Agunsoye J., Bello S., Haris M., Ramakokovhu M., Daramola M., Hassan S. Extraction of silica from cassava periderm using modified sol-gel method. Niger. J. Technol. Dev. 2018;15(2):57–65.
-
- Adrees M., Ali S., Rizwan M., Zia-ur-Rehman M., Ibrahim M., Abbas F., Farid M., Qayyum M.F., Irshad M.K. Mechanisms of silicon-mediated alleviation of heavy metal toxicity in plants: a review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015;119:186–197. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

